پيرو
جمهورية پيرو | |
|---|---|
النشيد: "Himno Nacional del Perú" (إسپانية) "النشيد الوطني لپيرو" March: "Marcha de Banderas" (إسپانية) "مسيرة الأعلام" | |
 | |
| العاصمة | ليما 12°2.6′S 77°1.7′W / 12.0433°S 77.0283°W |
| أكبر مدينة | العاصمة |
| اللغة لارسمية | الإسپانية |
| Co-official languages[أ] | |
| الجماعات العرقية |
|
| الدين |
|
| صفة المواطن | پيروڤيون |
| الحكومة | جمهورية رئاسية مركزية[2][3] |
• الرئيس | دينا بولوارتى |
| شاغر | |
| Pedro Angulo | |
| José Williams | |
| التشريع | كونگرس الجمهورية |
| الاستقلال from the مملكة إسپانيا | |
• اُعلن | 28 يوليو 1821 |
• التوحيد | 9 ديسمبر 1824 |
• الاعتراف | 14 أغسطس 1879 |
| المساحة | |
• الإجمالية | [convert: invalid number] (رقم 19) |
• الماء (%) | 0.41 |
| التعداد | |
• تقدير 2021 | |
• إحصاء 2017 | 31.237.385 |
• الكثافة | 23/km2 (59.6/sq mi) (رقم 198) |
| ن.م.إ. (ق.ش.م.) | تقدير 2020 |
• الإجمالي | |
• للفرد | |
| ن.م.إ. (الإسمي) | تقدير 2020 |
• الإجمالي | |
• للفرد | |
| جيني (2019) | 41.5[6] medium |
| م.ت.ب. (2019) | 0.777[7] high · رقم 59 |
| العملة | السول (PEN) |
| التوقيت | UTC−5 (التوقيت المحلي) |
| صيغة التاريخ | dd.mm.yyyy (CE) |
| جانب السواقة | يمين |
| مفتاح الهاتف | +51 |
| كود آيزو 3166 | PE |
| النطاق العلوي للإنترنت | .pe |
پيرو (Peru ؛ /pəˈruː/ (![]() استمع)؛ إسپانية: Perú النطق الإسپاني: [peˈɾu]؛ كتشوا: Piruw [pɪɾʊw];[8] آيمارا: Piruw [pɪɾʊw])، ورسمياً جمهورية پيرو (الإسپانية: República del Perú ), هي بلاد تقع في جبال الأنديز علي ساحل بيرو الغربي حيث يطل غربها علي المحيط الهادي. وهذه الجبال مغطاة بالجليد . وبشرقها توجد منحدرات تهبط عليها الأمطار حيث منابع نهر الأمازون الذي يمتد 5000 كم ليصب في المحيط الأطلنطي.[9] وفي السفوح توجد غابات إستوائية مطيرة بعبش فيها هنود أمريكيون بدائيون حتي الآن . وهؤلاء ليسوا من شعب بيرو الذي أقام حضاراته. تقع في غربي قارة أمريكا الجنوبية، كانت قبل غزو أسبانيا لها ، مركز حضارة لامبراطورية كبيرة هي امبراطورية الإنكا، حيث كانت تضم مايسمي حالياً بالإكوادور، وشيلي ،وبيرو ، والارجنتين ، وعاصمة هذه الامبراطورية مدينة كوزكو، غزتها أسبانيا في سنة 1523 ولم تستسلم الامبراطورية للأسبان إلا في سنة 1544 واستمر الاحتلال الاسباني حتي سنة 1820، عندما نالت بيرو استقلالها بعد كفاح طويل ضد أسبانيا.
استمع)؛ إسپانية: Perú النطق الإسپاني: [peˈɾu]؛ كتشوا: Piruw [pɪɾʊw];[8] آيمارا: Piruw [pɪɾʊw])، ورسمياً جمهورية پيرو (الإسپانية: República del Perú ), هي بلاد تقع في جبال الأنديز علي ساحل بيرو الغربي حيث يطل غربها علي المحيط الهادي. وهذه الجبال مغطاة بالجليد . وبشرقها توجد منحدرات تهبط عليها الأمطار حيث منابع نهر الأمازون الذي يمتد 5000 كم ليصب في المحيط الأطلنطي.[9] وفي السفوح توجد غابات إستوائية مطيرة بعبش فيها هنود أمريكيون بدائيون حتي الآن . وهؤلاء ليسوا من شعب بيرو الذي أقام حضاراته. تقع في غربي قارة أمريكا الجنوبية، كانت قبل غزو أسبانيا لها ، مركز حضارة لامبراطورية كبيرة هي امبراطورية الإنكا، حيث كانت تضم مايسمي حالياً بالإكوادور، وشيلي ،وبيرو ، والارجنتين ، وعاصمة هذه الامبراطورية مدينة كوزكو، غزتها أسبانيا في سنة 1523 ولم تستسلم الامبراطورية للأسبان إلا في سنة 1544 واستمر الاحتلال الاسباني حتي سنة 1820، عندما نالت بيرو استقلالها بعد كفاح طويل ضد أسبانيا.
Peruvian territory was home to several cultures during the ancient and medieval periods, and has one of the longest histories of civilization of any country, tracing its heritage back to the 10th millennium BCE. Notable pre-colonial cultures and civilizations include the Caral-Supe civilization (the earliest civilization in the Americas and considered one of the cradles of civilization,) the Nazca culture, the Wari and Tiwanaku empires, the Kingdom of Cusco, and the Inca Empire, the largest known state in the pre-Columbian Americas.
The Spanish Empire conquered the region in the 16th century and Charles V established a viceroyalty in 1542 with the official name of the Kingdom of Peru that encompassed most of its South American territories, with its capital in Lima. Higher education started in the Americas with the official establishment of the National University of San Marcos in Lima in 1551. Peru formally proclaimed independence in 1821, and following the foreign military campaigns of José de San Martín and Simón Bolívar, and the decisive battle of Ayacucho, Peru completed its independence in 1824 and its first congress decided to adopt Bolivar's republican system over San Martín's monarchist proposal that was supported by a large part of the population and aristocracy. In the ensuing years, the country first suffered from political instability until a period of relative economic and political stability began due to the exploitation of guano that ended with the War of the Pacific. In the 20th century, the country endured coups, social unrest, and internal conflicts, as well as periods of stability and economic upswing. In the 1990s, the country implemented a neoliberal economic model which is still in use to this day. As the 2000s commodities boom took place, Peru experienced a period of constant economic growth, while government finances, poverty reduction and progress in social sectors improved.[10][11][12][13] The nation has more recently adopted the Lima Consensus, an economic ideology of neoliberalism, deregulation and free market policies that has made foreign portfolio investment in Peru attractive.[12][13][14] Inflation in 2012 was the lowest in Latin America at 1.8%,[15] with the most recent annual rate standing at 1.9% in 2020.[16] Though statistical poverty has decreased significantly – from nearly 60% in 2004 to 20.5% in 2018.
The sovereign state of Peru is a representative democratic republic divided into 25 regions, which ranks 82nd on the Human Development Index.[17] It is one of the region's most prosperous economies with an average growth rate of 5.9% (in 2017)[18] and it has one of the world's fastest industrial growth rates at an average of 9.6% (as of 2018).[19] Its main economic activities include mining, manufacturing, agriculture and fishing, along with other growing sectors such as telecommunications and biotechnology.[20] The country forms part of The Pacific Pumas, a political and economic grouping of countries along Latin America's Pacific coast that share common trends of positive growth, stable macroeconomic foundations, improved governance and an openness to global integration. Peru ranks high in social freedom;[21] it is an active member of the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation, the Pacific Alliance, the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership and the World Trade Organization; and is considered as a middle power.[22]
Peru has a population that includes Mestizos, Amerindians, Europeans, Africans and Asians. The main spoken language is Spanish, although a significant number of Peruvians speak Quechuan languages, Aymara, or other Indigenous languages. This mixture of cultural traditions has resulted in a wide diversity of expressions in diverse fields, making the country a world-renowned gastronomical destiny, along with other topics such as art, literature, and music.
أصل الاسم
اسم البلد قد يكون مشتقاً من بيرو Birú، اسم حاكم محلي عاش بالقرب من خليج سان ميگل، مدينة پنما، في مطلع القرن السادس عشر.[23] الكونكيستادورات الاسبان، الذين وصلوا في 1522، اعتقدوا أنها أقصى النقاط جنوباً في العالم الجديد.[24] وحين غزا فرانشسكو پيزارو المناطق الواقعة إلى الجنوب منها، أصبحوا يسمونها بيرو Birú أو پيرو Perú.[25]
وثمة تاريخ بديل قدّمه الكاتب المعاصر للأحداث إنكا گارسيلاسو دلا ڤيگا، ابن أميرة من الإنكا وكونكيستادور. فيقول أن الاسم بيرو Birú هو اسم مواطن Amerindian عادي تصادف أن قابله طاقم سفينة في مهمة استكشافية للحاكم پدرو أرياس داڤيلا وطفق يربط أمثلة لسوء الفهم لانعدام لغة تواصل مشتركة.[26]
أسبغ التاج الاسباني على الاسم وضعاً شرعياً بتسليم توليدو في 1529، الذي وصف امبراطورية الإنكا حديثة الإخضاع لتصبح "مقاطعة پيرو".[27] في 1561، أعلن المتمرد لوپى دى أگيرى نفسه "الأمير" على پيرو المستقلة، والتي لم تستمر طويلاً إذ اِعتُقِل وأُعدِم. وتحت الحكم الاسباني، اتخذ البلد الاسم نائبية پيرو، التي أصبحت الجمهورية الپيروڤية بعد استقلالها حتى 1979، متخذةً الاسم الحالي جمهورية پيرو.[28]
السكان
يتكون سكانها من المستيزو وهم خليط من الهنود الأمريكيين والأسبان ويشكلون 42% من جملة السكان ، وهناك حوالي 47% من الهنود الأمريكيين ، وأقلية من الأسبان تصل إلى عشر السكان ثم خليط آخر من عناصر متعددة .
النشاط السكاني
تمثل حرفة صيد الأسماك مورداً هاماً لسكان بيرو ، ولقد تطورت هذه الحرفة آخيراً حتي أصبحت من أوائل الدول المنتجة للأسماك وإنتاجها يقارب سبع الإنتاج العالمي ، والزراعة تشغل حيزاً هاماً في اقتصاد البلاد غير أنها متخلفة ويعمل بالزراعة حوالي 36% من أهل البلاد ، وأهم الحاصلات الذرة ، والأرز ، والقمح ، والشعير ، والقطن ، وقصب السكر ، وثروتها الحيوانية من الأبقار والأغنام ، والماعز ، وتربي بمناطق الحشائش على سفوح المرتفعات ، وتشمل ثروتها المعدنية الفضة وهي رابعة دول العالم في إنتاجها ، كما تنتج النحاس ، والزنك ، والرصاص ،والذهب ، والإنتاج الصناعي يتركز في حفظ وتعليب الأسماك وصناعة الأقمشة والبتروكيميائيات والأغذية .
التاريخ
 مقالة مفصلة: تاريخ پيرو
مقالة مفصلة: تاريخ پيرو
قبل التاريخ وبيرو قبل كلومبس

شعب پيرو أصله من شعب الإنكا. وكانت لهجاته قد انصهرت في لغة الكونشو (لغة الإنكا). وقديما كان يعيش علي صيد الأسماك في ساحل المحيط الهادي. وأخذ يزرع بعدها. وكون قراه المتباعدة. وكثرة الحروب جعلته مجتمعا صناعيا. وقامت لديه ثقافات كبري التي قامت علي أكتاف شعب الإنكا الذي وحد أرضه. وأقام مبانيه الحجرية ما بين 850 ق.م. – 500 ق.م. وكان المبني ولاسيما في منطقة شافن بالمرتفعات الشمالية. وكان يصل إرتفاعه لثلاثة طوابق بها فتحات تهوية. وكان لحضارات بيرو أنواع متعددة من الفخار وكان لكل نوع إسمه ولونه. وفي مطلع القرن الأول الميلادي تفجرت هذه الحضارة حيث أقيمت الأهرامات الضخمة في عدة مناطق ولاسيما بالمناطق الساحلية الجافة نسبياً. وفي الساحل الشمالي ظهرت ثقافة موشيكا وبالساحل الجنوبي ظهرت ثقافتا باركاس ونازكا. وتميزت ثقافة موتشى بشق القنوات للري وتشييد قاعدة معبد هواكس لعبادة الشمس والقمر. وكانت من الطوب اللبن . كما شكلت الأواني علي هيئة طلبعبة للحيوانات والبشر وصور من الحياة. وثقافة باركاس لا يعرف عنها إلا القليل إلا أنها خلفت مقابر ملحق بها الآبار وبعض المومياوات التي عثر عليها بشبه جزيرة باركاس. وفي جنوبها وجدت ثقافة نازكا التي كانت بيوتها من اللبن. وقد خلفت أقمشة بديعة وفخار ملون بطريقة بدائية. وفي الجنوب من بيرو قامت ثقافة پاركاس ما بين سنتي 700 - 500 ق.م. وقد تميزت بأسلوب النحت الدقيق. وبصفة عامة إشتهرت بيرو بحضاراتها ولاسيما حضارة الإنكا التي ظهرت في أمريكا الجنوبية . وامتدت حضارة بيرو إلى الإكوادور وكولومبيا وبوليفيا.
الحكم والسياسة
الحكم
Peru is a unitary presidential representative democratic republic with a multi-party system.[2][3] Under the current constitution, the president is both head of state and government; he or she is elected for five years and cannot serve consecutive terms.[29] The president designates the Prime Minister and, on his or her advice, the rest of the Council of Ministers.[30] The Congress of the Republic is unicameral with 130 members elected for five-year terms.[31] Bills may be proposed by either the executive or the legislative branch; they become law after being passed by Congress and promulgated by the president.[32] The judiciary is nominally independent,[33] though political intervention into judicial matters has been common throughout history and arguably continues in modern day.[34]
The Peruvian government is directly elected, and voting is compulsory for all citizens aged 18 to 70.[35] Congress is currently composed of Fuerza Popular (59 seats), Peruanos Por el Kambio (17 seats), Frente Amplio (10 seats), New Peru (10 seats), Alianza para el Progreso (9 seats), Acción Popular (5 seats) and APRA (5 seats) and 18 not grouped.[36]
القانون
The law of Peru includes the constitution, and a number of codes and decrees.
العلاقات الخارجية

Peruvian foreign relations have historically been dominated by border conflicts with neighboring countries, most of which were settled during the 20th century.[37] Recently,[when?] Peru disputed its maritime limits with Chile in the Pacific Ocean.[38] Peru is an active member of several regional blocs and one of the founders of the Andean Community of Nations. It is also a participant in international organizations such as the Organization of American States and the United Nations. Javier Pérez de Cuéllar served as UN Secretary General from 1981 to 1991. Former President Fujimori's tainted re-election to a third term in June 2000 strained Peru's relations with the United States and with many Latin American and European countries, but relations improved with the installation of an interim government in November 2000 and the inauguration of Alejandro Toledo in July 2001 after free and fair elections.
Peru is planning full integration into the Andean Free Trade Area. In addition, Peru is a standing member of APEC and the World Trade Organization, and is an active participant in negotiations toward a Free Trade Area of the Americas (FTAA).
During the crisis in Bolivarian Venezuela, Peru participated in a leading role to help mediate the situation in Venezuela by being active within the مجموعة ليما.
العسكرية وإنفاذ القانون

The Peruvian Armed Forces are the military services of Peru, comprising independent Army, Navy and Air Force components. Their primary mission is to safeguard the independence, sovereignty and territorial integrity of the country. As a secondary mission they participate in economic and social development as well as in civil defense tasks.[39] Conscription was abolished in 1999 and replaced by voluntary military service.[40] The armed forces are subordinate to the Ministry of Defense and to the President as Commander-in-Chief.
The National Police of Peru is often classified as a part of the armed forces. Although in fact it has a different organization and a wholly civil mission, its training and activities over more than two decades as an anti-terrorist force have produced markedly military characteristics, giving it the appearance of a virtual fourth military service with significant land, sea and air capabilities and approximately 140,000 personnel. The Peruvian armed forces report through the Ministry of Defense, while the National Police of Peru reports through the Ministry of Interior.
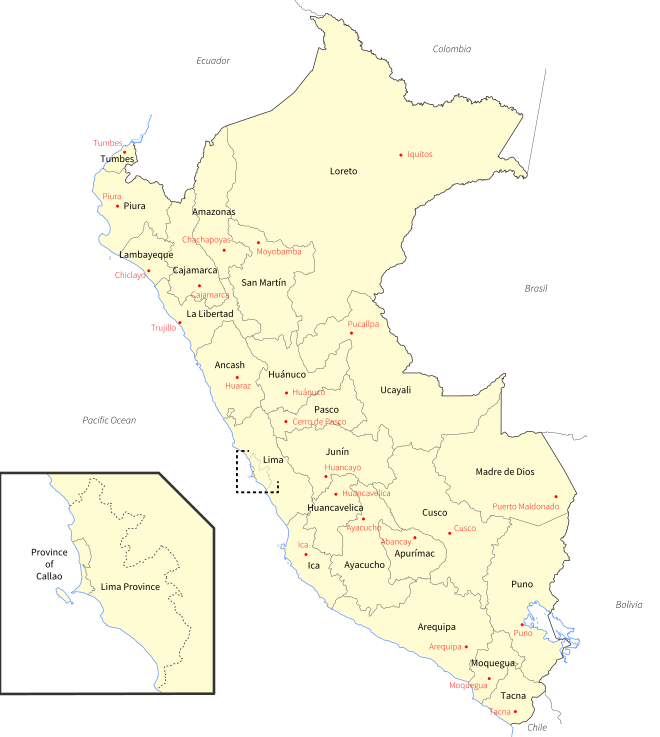
التقسيمات الادارية
Peru is divided into 24 regions and the Constitutional Province of El Callao. Each region has an elected government composed of a president and council that serve four-year terms.[41] These governments plan regional development, execute public investment projects, promote economic activities, and manage public property.[42] The province of Lima is administered by a city council.[43] The goal of devolving power to regional and municipal governments was among others to improve popular participation. NGOs played an important role in the decentralization process and still influence local politics.[44]
| التقسيمات الادارية في پيرو | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| الأقسام | العاصمة | المساحة (كم²) | التعداد (إحصاء 2017) |
الكثافة | الإنشاء | ||||
| Amazonas | Chachapoyas | 39 249,13 | 379 384 | 9,7 | 1832 | ||||
| Ancash | Huaraz | 35 914,81 | 1 083 519 | 30,2 | 1821 | ||||
| Apurímac | Abancay | 20 895,79 | 405 759 | 19,4 | 1873 | ||||
| Arequipa | Arequipa | 63 345,39 | 1 382 730 | 21,8 | 1822 | ||||
| Ayacucho | Ayacucho | 43 814,80 | 616 176 | 14,1 | 1822 | ||||
| Cajamarca | Cajamarca | 33 317,54 | 1 341 012 | 40,3 | 1962 | ||||
| Constitutional Province of Callao | Callao | 146,98 | 994 494 | 6815,8 | 1857 | ||||
| Cusco | Cusco | 71 986,50 | 1 205 527 | 16,7 | 1822 | ||||
| Huancavelica | Huancavelica | 22 131,47 | 347 639 | 15,7 | 1822 | ||||
| Huánuco | Huánuco | 36 848,85 | 721 047 | 19,3 | 1869 | ||||
| Ica | Ica | 21 327,83 | 850 765 | 39,9 | 1866 | ||||
| Junín | Huancayo | 44 197,23 | 1 246 038 | 32,4 | 1825 | ||||
| La Libertad | Trujillo | 25 449,9 | 1 778 080 | 69,7 | 1821 | ||||
| Lambayeque | Chiclayo | 14 231,3 | 1 197 260 | 82,8 | 1874 | ||||
| ليما | ليما | 34 801,59 | 9 485 405 | 242,4 | 1821 | ||||
| Loreto | Iquitos | 368 851,95 | 883 510 | 2,4 | 1866 | ||||
| Madre de Dios | Puerto Maldonado | 85 300,54 | 141 70 | 1,7 | 1912 | ||||
| Moquegua | Moquegua | 15 733,97 | 174 863 | 11,1 | 1837 | ||||
| Pasco | Cerro de Pasco | 25 319,59 | 254 065 | 10,2 | 1944 | ||||
| Piura | Piura | 35 892,49 | 1 856 809 | 52,1 | 1861 | ||||
| Puno | Puno | 71 999,00 | 1 172 697 | 17,5 | 1822 | ||||
| سان مارتين | Moyobamba | 51 253,31 | 813 381 | 15,9 | 1906 | ||||
| تاكنا | Tacna | 16 075,89 | 329 332 | 20,5 | 1875 | ||||
| Tumbes | Tumbes | 4669,20 | 224 863 | 48,2 | 1942 | ||||
| Ucayali | Pucallpa | 102 410,55 | 496 459 | 4,9 | 1980 | ||||
| پيرو | ليما | 1 285 216,20 | 31 237 385 | 25,02 | 1821 | ||||
المناطق العمرانية
Several metropolitan areas are defined for Peru – these overlap the district areas, and have limited authority. The largest of them, the Lima metropolitan area, is the seventh-largest metropolis in the Americas.
الجغرافيا
الموقع
في غرب أمريكا الجنوبية تحدها كولومبيا والإكوادور من الشمال ، وبوليفيا والبرازيل من الشرق ، وشيلي من الجنوب ، والمحيط الهادي من الغرب ، وتبلغ مساحتها (1,285,126 كم ) ، وقدر عدد سكانها في سنة 1988، 21,2 مليون نسمة والعاصمة (ليما ) وتوجد على ساحل المحيط الهادي ومن المدن الهامة كالاو، وأركيبا، وتروخيو. والأسبانية لغة البلاد الرسمية ، وإلى جانبها لغات محلية يتحدث بها الهنود الأمريكيون وهي (الكشوية ) و(الايمارا ) وتنقسم البلاد إلي 22 مقاطعة إدارية
الأرض
تنقسم بيرو إلى ثلاثة أقاليم تضاريسية ،تبدأ من الغرب بإقليم الساحل وهو شريط ضيق من الاراضي الصحراوية ، ويغلب عليه المظهر الجاف في طابعه المناخي ، والإقليم الثاني هو مرتفعات سيرا ويشكل قسماً من جبال الإنديز الكبري ، كما تحصر السلاسل الجبلية بينها هضبة تضم بحيرة (تيني كاكا )أكبر البحيرات العذبة بأمريكا الجنوبية وهناك بعض القمم التي تغطيها الثلوج الدائمة مثل قمة المسني . والإقليم الثالث يتكون من منحدرات جبال الإنديز الشرقية وتنحدر نحو الشرق حيث تصرف مياهها إلى نهر الأمازون .
المناخ
 مقالة مفصلة: مناخ پيرو
مقالة مفصلة: مناخ پيرو
رغم مرور الدائرة الاستوائية يشمال بيرو ، إلا أن تضرس سطحها ومرور تيار بيرو البحري بسواحلها مما أثر في أحوالها المناخية ، فالنطاق الساحلي منخفض الحرارة كثير الضباب مرتفع الرطوبة قليل المطر ، أما المرتفعات فوفيرة الأمطار تعتدل بها الحرارة نسبياً ، وفي النطاق الشرقي حيث تنخفض الأرض تدريجياً نحو حوض الأمازون، وترتفع الحرارة في هذا النطاق .
الاقتصاد
The economy of Peru is the 48th largest in the world (ranked by Purchasing power parity),[45] and the income level is classified as upper middle by the World Bank.[46] Peru is, اعتبارا من 2011[تحديث], one of the world's fastest-growing economies owing to an economic boom experienced during the 2000s.[47] It has an above-average Human Development Index of 0.77 which has seen steady improvement over the last 25 years.[clarify][48] Historically, the country's economic performance has been tied to exports, which provide hard currency to finance imports and external debt payments.[49] Although they have provided substantial revenue, self-sustained growth and a more egalitarian distribution of income have proven elusive.[50] According to 2015 data, 19.3% of its total population is poor, including 9% that lives in extreme poverty.[51] Inflation in 2012 was the lowest in Latin America at only 1.8%, but increased in 2013 as oil and commodity prices rose; اعتبارا من 2014[تحديث] it stands at 2.5%.[52] The unemployment rate has fallen steadily in recent years,[clarify] and اعتبارا من 2012[تحديث] stands at 3.6%.
Peruvian economic policy has varied widely over the past decades.[clarify] The 1968–1975 government of Juan Velasco Alvarado introduced radical reforms, which included agrarian reform, the expropriation of foreign companies, the introduction of an economic planning system, and the creation of a large state-owned sector. These measures failed to achieve their objectives of income redistribution and the end of economic dependence on developed nations.[53]
Despite these results, most reforms were not reversed until the 1990s, when the liberalizing government of Alberto Fujimori ended price controls, protectionism, restrictions on foreign direct investment, and most state ownership of companies.[54]
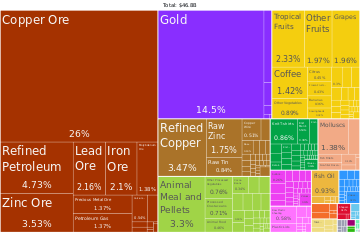
اعتبارا من 2010[تحديث] Services account for 53% of Peruvian gross domestic product, followed by manufacturing (22.3%), extractive industries (15%), and taxes (9.7%).[55] Recent economic growth had been fueled by macroeconomic stability, improved terms of trade, and rising investment and consumption.[56] Trade was expected to increase further after the implementation of a free trade agreement with the United States signed on 12 April 2006.[57] Peru's main exports were copper, gold, zinc, textiles, and fish meal; its major trade partners were the United States, China, Brazil, and Chile.[58] Peru was ranked 70th in the Global Innovation Index in 2021.[59]
التعدين
The country is heavily dependent on mining for the export of raw materials, which represent 60% of exports: in 2019, the country was the second world producer of copper,[60] silver[61] and zinc,[62] eighth world producer of gold,[63] third world producer of lead,[64] the world's fourth largest producer of tin,[65] the fifth world's largest producer of boron[66] and the world's fourth largest producer of molybdenum.[67] – not to mention gas and of oil. Little industrialized, Peru suffers from the international variation of commodity prices.[68]
الزراعة
Peru is the world's largest producer of quinoa, one of the 5 largest producers of avocado, blueberry, artichoke and asparagus, one of the 10 largest producers in the world of coffee and cocoa, and one of the 15 largest producers in the world of potato and pineapple, also having a considerable production of grape, sugarcane, rice, banana, maize and cassava; its agriculture is considerably diversified. In livestock, Peru is one of the 20 largest producers of chicken meat in the world.[69]
الصناعة
The World Bank lists the top producing countries each year, based on the total value of production. By the 2019 list, Peru has the 50th most valuable industry in the world ($28.7 billion).[70]
In 2016 Peru was the world's largest supplier of fishmeal.[71]
السكان
With about 31.2 million inhabitants in 2017, Peru is the fourth most populous country in South America.[72] The demographic growth rate of Peru declined from 2.6% to 1.6% between 1950 and 2000; with the population being expected to reach approximately 42 million in 2050.[73] According to the 1940 Peruvian census, Peru had a population at the time of seven million residents.[74]
اعتبارا من 2017[تحديث], 79.3% lived in urban areas and 20.7% in rural areas.[75] Major cities include the Lima metropolitan area (home to over 9.8 million people), Arequipa, Trujillo, Chiclayo, Piura, Iquitos, Cusco, Chimbote, and Huancayo; all reported more than 250,000 inhabitants in the 2007 census.[76] There are 15 uncontacted Amerindian tribes in Peru.[77] Peru has a life expectancy of 75.0 years (72.4 for males and 77.7 for females) according to the latest data for the year 2016 from the World Bank.[78]
أكبر المدن أو البلدات في پيرو
Estimated 2014 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Region | Pop. | Rank | Region | Pop. | ||||
 ليما  أركيپا |
1 | ليما | ليما | 9,735,587 (Metro pop.) [79] | 11 | خولياكا | Puno | 267,174 |  تروهيو  تشيكلايو |
| 2 | أركيپا | أركيپا | 1,008,029 (Metro pop.) | 12 | إيكا | إيكا | 241,903 | ||
| 3 | تروهيو | لا ليبرتاد | 935,147 (Metro pop.) | 13 | كاخاماركا | كاخاماركا | 218,775 | ||
| 4 | تشيكلايو | Lambayeque | 801,580 (Metro pop.) | 14 | Pucallpa | Ucayali | 211,631 | ||
| 5 | هوانكايو | خونين | 501.384 | 15 | سولانا | پيورا | 199,606 | ||
| 6 | Iquitos | Loreto | 432,476 | 16 | Ayacucho | Ayacucho | 177,420 | ||
| 7 | پيورا | پيورا | 430,319 | 17 | Chincha Alta | Ica | 174,575 | ||
| 8 | كوسكو | كوسكو | 420,137 | 18 | Huánuco | Huánuco | 172,924 | ||
| 9 | تشيمبوتى | أنكاش | 367,850 | 19 | Tarapoto | San Martín | 141,053 | ||
| 10 | تاكنا | تاكنا | 288,698 | 20 | Puno | Puno | 138,723 | ||
الجماعات العرقية
Peru is a multiethnic nation formed by successive waves of different peoples over five centuries. Amerindians inhabited Peruvian territory for several millennia before the Spanish conquest in the 16th century; according to historian Noble David Cook, their population decreased from nearly 5–9 million in the 1520s to around 600,000 in 1620 mainly because of infectious diseases.[81]
The 2017 census for the first time included a question on ethnic self-identification. According to the results, 60.2% of the people identified themselves as mestizo, 22.3% identified themselves as Quechua, 5.9% identified themselves as white, 3.6% identified themselves as black, 2.4% identified themselves as Aymara, 2.3% identified themselves as other ethnic groups, and 3.3% didn't declare their ethnicity.[80]
Spaniards and Africans arrived in large numbers under colonial rule, mixing widely with each other and with Indigenous peoples. After independence, there was gradual immigration from England, France, Germany, and Italy.[82] Peru freed its black slaves in 1854.[83] Chinese and Japanese arrived in the 1850s as laborers following the end of slavery, and have since become a major influence in Peruvian society.[84]
اللغة
According to the Peruvian Constitution of 1993, Peru's official languages are Spanish and, in areas where they predominate, Quechua and other Indigenous languages. Spanish is spoken natively by 82.6% of the population, Quechua by 13.9%, and Aymara by 1.7%, while other languages are spoken by the remaining 1.8%.[85]
Spanish language is used by the government and is the mainstream language of the country, which is used by the media and in educational systems and commerce. Amerindians who live in the Andean highlands speak Quechua and Aymara and are ethnically distinct from the diverse Indigenous groups who live on the eastern side of the Andes and in the tropical lowlands adjacent to the Amazon basin.[86]
Peru's distinct geographical regions are mirrored in a language divide between the coast where Spanish is more predominant over the Amerindian languages, and the more diverse traditional Andean cultures of the mountains and highlands. The Indigenous populations east of the Andes speak various languages and dialects. Some of these groups still adhere to traditional Indigenous languages, while others have been almost completely assimilated into the Spanish language. There has been an increasing and organized effort to teach Quechua in public schools in the areas where Quechua is spoken. In the Peruvian Amazon, numerous Indigenous languages are spoken, including Asháninka, Bora, and Aguaruna.[86]
الدين
Roman Catholicism has been the predominant faith in Peru for centuries, albeit religious practices have a high degree of syncretism with Indigenous traditions. Two of its universities, Pontifical Catholic University of Peru and Universidad Cattolica San Pablo, are among the 5 top universities of the country.[87] As of the 2017 census, 76% of the population over 12 years old described themselves as Catholic, 14.1% as Evangelical, 4.8% as Protestant, Jewish, Latter-day Saints, and Jehovah's Witnesses, and 5.1% as nonreligious.[88]
Amerindian religious traditions continue to play a major role in the beliefs of Peruvians. Catholic festivities like Corpus Christi, Holy Week and Christmas sometimes blend with Amerindian traditions. Amerindian festivities from pre-Columbian remain widespread; Inti Raymi, an ancient Inca festival, is still celebrated, especially in rural communities.
The majority of towns, cities, and villages have their own official church or cathedral and patron saint.
التعليم
Peru's literacy rate is estimated at 92.9% as of 2007; this rate is lower in rural areas (80.3%) than in urban areas (96.3%).[89] Primary and secondary education are compulsory and free in public schools.[45][90]
Peru is home to one of the oldest institutions of higher learning in the New World. The National University of San Marcos, founded on 12 May 1551, during the Viceroyalty of Peru, is the first officially established and the oldest continuously functioning university in the Americas.[citation needed]
أسماء الأماكن
Many of the Peruvian toponyms have Indigenous sources. In the Andes communities of Ancash, Cusco and Puno, Quechua or Aymara names are overwhelmingly predominant. Their Spanish-based orthography, however, is in conflict with the normalized alphabets of these languages. According to Article 20 of Decreto Supremo No 004-2016-MC (Supreme Decree) which approves the Regulations to Law 29735, published in the official newspaper El Peruano on 22 July 2016, adequate spellings of the toponyms in the normalized alphabets of the Indigenous languages must progressively be proposed with the aim of standardizing the naming used by the National Geographic Institute (Instituto Geográfico Nacional, IGN). The National Geographic Institute realizes the necessary changes in the official maps of Peru.[91]
الثقافة
Peruvian culture is primarily rooted in Andean and Iberian traditions,[92] though it has also been influenced by various Asian and African ethnic groups. Peruvian artistic traditions date back to the elaborate pottery, textiles, jewelry, and sculpture of Pre-Inca cultures. The Incas maintained these crafts and made architectural achievements including the construction of Machu Picchu. Baroque dominated colonial art, though modified by Native traditions.[93]
During this period, most art focused on religious subjects; the numerous churches of the era and the paintings of the Cusco School are representative.[94] Arts stagnated after independence until the emergence of Indigenismo in the early 20th century.[95] Since the 1950s, Peruvian art has been eclectic and shaped by both foreign and local art currents.
الفنون المرئية
Peruvian art has its origin in the Andean civilizations. These civilizations arose in the territory of modern Peru before the arrival of the Spanish. Peruvian art incorporated European elements after the Spanish conquest and continued to evolve throughout the centuries up to the modern day.
الفن قبل كلومبس

Peru's earliest artwork came from the Cupisnique culture, which was concentrated on the Pacific coast, and the Chavín culture, which was largely north of Lima between the Andean mountain ranges of the Cordillera Negra and the Cordillera Blanca. Decorative work from this era, approximately the 9th century BCE, was symbolic and religious in nature. The artists worked with gold, silver, and ceramics to create a variety of sculptures and relief carvings. These civilizations were also known for their architecture and wood sculptures.
Between the 9th century BCE and the 2nd century CE, the Paracas Cavernas and Paracas Necropolis cultures developed on the south coast of Peru. Paracas Cavernas produced complex polychrome and monochrome ceramics with religious representations. Burials from the Paracas Necropolis also yielded complex textiles, many produced with sophisticated geometric patterns.
The 3rd century BCE saw the flowering of the urban culture, Moche, in the Lambayeque region. The Moche culture produced impressive architectural works, such as the Huacas del Sol y de la Luna and the Huaca Rajada of Sipán. They were experts at cultivation in terraces and hydraulic engineering and produced original ceramics, textiles, pictorial and sculptural works.
Another urban culture, the Wari civilization, flourished between the 8th and 12th centuries in Ayacucho. Their centralized town planning was extended to other areas, such as Pachacamac, Cajamarquilla and Wari Willka.
Between the 9th and 13th centuries CE, the military urban Tiwanaku empire rose by the borders of Lake Titicaca. Centered around a city of the same name in modern-day Bolivia, the Tiwanaku introduced stone architecture and sculpture of a monumental type. These works of architecture and art were made possible by the Tiwanaku's developing bronze, which enabled them to make the necessary tools.
Urban architecture reached a new height between the 14th and 15th centuries in the Chimú Culture. The Chimú built the city of Chan Chan in the valley of the Moche River, in La Libertad. The Chimú were skilled goldsmiths and created remarkable works of hydraulic engineering.
The Inca Civilization, which united Peru under its hegemony in the centuries immediately preceding the Spanish conquest, incorporated into their own works a great part of the cultural legacy of the civilizations which preceded it. Important relics of their artwork and architecture can be seen in cities like Cusco, architectural remains like Sacsahuamán and Machu Picchu and stone pavements that united Cusco with the rest of the Inca Empire.
الفن الاستعماري

Peruvian sculpture and painting began to define themselves from the ateliers founded by monks, who were strongly influenced by the Sevillian Baroque School. In this context, the stalls of the Cathedral choir, the fountain of the Main Square of Lima both by Pedro de Noguera, and a great part of the colonial production were registered. The first center of art established by the Spanish was the Cuzco School that taught Quechua artists European painting styles. Diego Quispe Tito (1611–1681) was one of the first members of the Cuzco school and Marcos Zapata (1710–1773) was one of the last.[97]
Painting of this time reflected a synthesis of European and Indigenous influences, as is evident in the portrait of prisoner Atahualpa, by D. de Mora or in the canvases of the Italians Mateo Pérez de Alesio and Angelino Medoro, the Spaniards Francisco Bejarano and J. de Illescas and the Creole J. Rodriguez.
During the 17th and 18th centuries, the Baroque Style also dominated the field of plastic arts.
الأدب
The term Peruvian literature not only refers to literature produced in the independent Republic of Peru, but also to literature produced in the Viceroyalty of Peru during the country's colonial period, and to oral artistic forms created by diverse ethnic groups that existed in the area during the pre-Columbian period, such as the Quechua, the Aymara and the Chanka people.
Peruvian literature is rooted in the oral traditions of pre-Columbian civilizations. Spaniards introduced writing in the 16th century; colonial literary expression included chronicles and religious literature. After independence, Costumbrism and Romanticism became the most common literary genres, as exemplified in the works of Ricardo Palma.[98] The early 20th century's Indigenismo movement was led by such writers as Ciro Alegría[99] and José María Arguedas.[100] César Vallejo wrote modernist and often politically engaged verse. Modern Peruvian literature is recognized thanks to authors such as Nobel laureate Mario Vargas Llosa, a leading member of the Latin American Boom.[101]

المطبخ
Because of the Spanish expedition and discovery of America, explorers started the Columbian exchange which included unknown food in the Old World, including potatoes, tomatoes, and maize. Modern Indigenous Peruvian food often includes corn, potatoes, and chilies. There are now more than 3,000 kinds of potatoes grown on Peruvian terrain, according to Peru's Instituto Peruano de la Papa.[102] Modern Peruvian cuisine blends Amerindian and Spanish food with strong influences from Chinese, African, Arab, Italian, and Japanese cooking.[103] Common dishes include anticuchos, ceviche, and pachamanca. Peru's varied climate allows the growth of diverse plants and animals good for cooking.[104]
Peruvian cuisine reflects local practices and ingredients – including influences from the Indigenous population including the Inca and cuisines brought in with colonizers and immigrants. Without the familiar ingredients from their home countries, immigrants modified their traditional cuisines by using ingredients available in Peru. The four traditional staples of Peruvian cuisine are corn, potatoes and other tubers, Amaranthaceaes (quinoa, kañiwa and kiwicha) and legumes (beans and lupins). Staples brought by the Spanish include rice, wheat, and meats (beef, pork, and chicken). Many traditional foods – such as quinoa, kiwicha, chili peppers, and several roots and tubers have increased in popularity in recent decades, reflecting a revival of interest in Native Peruvian foods and culinary techniques. It is also common to see traditional cuisines being served with a modern flair in towns like Cusco, where tourists come to visit. Chef Gaston Acurio has become well known for raising awareness of local ingredients.
الموسيقى

Peruvian music has Andean, Spanish, and African roots.[105] In pre-Columbian times, musical expressions varied widely in each region; the quena and the tinya were two common instruments.[106] Spaniards introduced new instruments, such as the guitar and the harp, which led to the development of crossbred instruments like the charango.[107] African contributions to Peruvian music include its rhythms and the cajón, a percussion instrument. Peruvian folk dances include marinera, tondero, zamacueca, diablada and huayno.[108]
Peruvian music is dominated by the national instrument, the charango. The charango is a member of the lute family of instruments and was invented during colonial times by musicians imitating the Spanish vihuela. In the Canas and Titicaca regions, the charango is used in courtship rituals, symbolically invoking mermaids with the instrument to lure the woman to the male performers. Until the 1960s, the charango was denigrated as an instrument of the rural poor. After the revolution in 1959, which built the Indigenismo movement (1910–1940), the charango was popularized among other performers. Variants include the walaycho, chillador, chinlili, and the larger and lower-tuned charangon.
While the Spanish guitar is widely played, so too is the Spanish-in-origin bandurria. Unlike the guitar, it has been transformed by Peruvian players over the years, changing from a 12-string, 6-course instrument to one having 12 to 16 strings in a mere four courses. Violins and harps, also of European origin, are also played.
Cinema
While the Peruvian film industry has not been nearly as prolific as that of some other Latin American countries, some Peruvian movies produced enjoyed regional success. Historically, the cinema of Peru began in Iquitos in 1932 by Antonio Wong Rengifo (with a momentous, initial film billboard from 1900) because of the rubber boom and the intense arrival of foreigners with technology to the city, and thus continued an extensive, unique filmography, with a different style than the films made in the capital, Lima.
Peru also produced the first animated 3-D film in Latin America, Piratas en el Callao. This film is set in the historical port city of Callao, which during colonial times had to defend itself against attacks by Dutch and British privateers seeking to undercut Spain's trade with its colonies. The film was produced by the Peruvian company Alpamayo Entertainment, which made a second 3-D film one year later: Dragones: Destino de Fuego.
In February 2006, the film Madeinusa, produced as a joint venture between Peru and Spain and directed by Claudia Llosa, was set in an imaginary Andean village and describes the stagnating life of Madeinusa performed by Magaly Solier and the traumas of post-civil war Peru.
Llosa, who shared elements of Gabriel García Márquez's magic realism, won an award at the Rotterdam Film Festival. Llosa's second feature, The Milk of Sorrow ("La Teta Asustada"), was nominated for the 82nd Academy Awards for Best Foreign Language Picture, the first Peruvian film in the academy's history to be nominated. The Milk of Sorrow ("La Teta Asustada"), won the Golden Bear award at the 2009 Berlinale.
المصادر
- الأقليات المسلمة في الأمريكتين والبحر الكاريبي - سيد عبد المجيد بكر .
- موسوعة حضارة العالم، وضعها أحمد محمد عوف.
وصلات خارجية
- حكومية
- (بالإسپانية) Web portal of the Peruvian Government
- (بالإسپانية) Directory of Peruvian Government websites
- مراجع عامة
- BBC country profile of Peru
- Encyclopædia Britannica entry on Peru
- Peru web directory
- غيرها
- Peru travel guide from Wikitravel
- پيرو at the Open Directory Project
خطأ استشهاد: وسوم <ref> موجودة لمجموعة اسمها "lower-alpha"، ولكن لم يتم العثور على وسم <references group="lower-alpha"/>
- ^ "Perú: Perfil Sociodemográfico" (PDF). Instituto Nacional de Estadística e Informática. p. 231. Archived (PDF) from the original on 11 February 2020. Retrieved 27 September 2018.
- ^ أ ب Shugart, Matthew Søberg (September 2005). "Semi-Presidential Systems: Dual Executive and Mixed Authority Patterns" (PDF). Graduate School of International Relations and Pacific Studies. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 August 2008. Retrieved 31 August 2017.
- ^ أ ب Shugart, Matthew Søberg (December 2005). "Semi-Presidential Systems: Dual Executive And Mixed Authority Patterns". French Politics. 3 (3): 323–351. doi:10.1057/palgrave.fp.8200087. ISSN 1476-3427. OCLC 6895745903.
Only in Latin America have all new democracies retained a pure presidential form, except for Peru (president-parliamentary) and Bolivia (assembly-independent).
- ^ "Perú: Estimaciones y Proyecciones de Población Total, por Años Calendario y Edades Simples, 1950–2050" [Peru: Estimates and Projections of Total Population, by Calendar Years and Simple Ages, 1950-2050] (PDF) (in الإسبانية). National Institute of Statistics and Informatics. September 2009. Archived (PDF) from the original on 18 September 2018. Retrieved 18 September 2018.
- ^ أ ب ت ث "Peru". International Monetary Fund. Archived from the original on 17 January 2021. Retrieved 18 January 2020.
- ^ "Gini Index". World Bank. Archived from the original on 7 May 2020. Retrieved 14 July 2021.
- ^ Human Development Report 2020 The Next Frontier: Human Development and the Anthropocene (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. 15 December 2020. pp. 343–346. ISBN 978-92-1-126442-5. Archived (PDF) from the original on 15 December 2020. Retrieved 16 December 2020.
- ^ Quechua name used by government of Peru is Perú (see Quechua-language version of Peru Parliament website Archived 30 يوليو 2010 at the Wayback Machine and Quechua-language version of Peru Constitution but common Quechua name is Piruw
- ^ "Perú: País megadiverso" [Peru: Megadiverse country] (PDF) (in الإسبانية). Servicio Nacional de Áreas Naturales Protegidas. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 June 2014.
- ^ Dennis, Claire (2017-08-23). "Another Top Peru Politician Embroiled in Odebrecht Scandal". InSight Crime (in الإنجليزية الأمريكية). Archived from the original on 15 December 2022. Retrieved 2022-12-15.
- ^ The World Bank, Countries: Peru Archived 30 أكتوبر 2019 at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved 1 October 2011
- ^ أ ب Orihuela, José Carlos (January–June 2020). "El consenso de Lima y sus descontentos: del restringido desarrollismo oligarca a revolucionarias reformas estructurales". Revista de historia. Concepción, Chile. 27 (1): 77–100.
- ^ أ ب Tegel, Simeon. "How Peru Laid the Groundwork for an Oil Spill Disaster". Foreign Policy (in الإنجليزية الأمريكية). Archived from the original on 22 February 2022. Retrieved 23 February 2022.
- ^ Peru Country Risk Report – Q3 2021. London: Fitch Solutions. 2021.
- ^ "Peru and the IMF". International Monetary Fund. Archived from the original on 8 July 2014. Retrieved 27 July 2014.
- ^ "World Economic Outlook Database, October 2019". IMF.org. International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 24 October 2019.
- ^ "World Economic and Financial Surveys, World Economic Outlook October 2015" (PDF). www.imf.org. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 January 2017. Retrieved 15 February 2018.
- ^ "Peru Overview". World Bank. Archived from the original on 5 May 2017. Retrieved 17 April 2017.
- ^ "Peru". The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. Archived from the original on 7 July 2018. Retrieved 8 January 2018.
- ^ David E. Castro Garro. "Módulo de capacitación en recursos genéticos y bioseguridad" [Training module on genetic resources and biosafety] (PDF) (in الإسبانية). Ministerio de Ambiente de la República de Perú. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 April 2018.
- ^ "Freedom in the World 2017 – Populists and Autocrats: The Dual Threat to Global Democracy" Archived 27 يوليو 2017 at the Wayback Machine by Freedom House, 31 January 2017
- ^ McKercher, B. J. C. (2012). Routledge Handbook of Diplomacy and Statecraft (in الإنجليزية). Routledge. ISBN 9781136664366. Archived from the original on 17 April 2021. Retrieved 30 May 2020.
a Middle Power like Peru lack the diplomatic and other resources...
- ^ Porras Barrenechea, Raúl. El nombre del Perú. Lima: Talleres Gráficos P.L. Villanueva, 1968, p. 83.
- ^ Raúl Porras Barrenechea, El nombre del Perú, p. 84.
- ^ Raúl Porras Barrenechea, El nombre del Perú, p. 86.
- ^ Vega, Garcilasco, Commentarios Reales de los Incas, Editorial Mantaro, Lima, ed. 1998. pp. 14–15. First published in Lisbon in 1609.
- ^ Raúl Porras Barrenechea, El nombre del Perú, p. 87.
- ^ قالب:Cite constitution
- ^ Constitución Política del Perú, Article No. 112.
- ^ Constitución Política del Perú, Article No. 122.
- ^ Constitución Política del Perú, Article No. 90.
- ^ Constitución Política del Perú, Articles No. 107–108.
- ^ Constitución Política del Perú, Article No. 146.
- ^ Clark, Jeffrey. Building on quicksand. Retrieved 24 July 2007.
- ^ Constitución Política del Perú, Article No. 31.
- ^ (بالإسپانية) Congreso de la República del Perú, Grupos Parlamentarios Archived 29 ديسمبر 2007 at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved 27 August 2011.
- ^ خطأ استشهاد: وسم
<ref>غير صحيح؛ لا نص تم توفيره للمراجع المسماةJohn - ^ BBC News (4 November 2005), Peru–Chile border row escalates Archived 15 يناير 2009 at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved 16 May 2007.
- ^ Ministerio de Defensa, Libro Blanco de la Defensa Nacional. Ministerio de Defensa, 2005, 90.
- ^ Ley N° 27178, Ley del Servicio Militar, Articles No. 29, 42 and 45.
- ^ Ley N° 27867, Ley Orgánica de Gobiernos Regionales, Article No. 11.
- ^ Ley N° 27867, Ley Orgánica de Gobiernos Regionales, Article No. 10.
- ^ Ley N° 27867, Ley Orgánica de Gobiernos Regionales, Article No. 66.
- ^ Monika Huber; Wolfgang Kaiser (February 2013). "Mixed Feelings". dandc.eu.
- ^ أ ب Peru Archived 23 يناير 2021 at the Wayback Machine . CIA, The World Factbook
- ^ The World Bank, Data by country: Peru Archived 8 نوفمبر 2016 at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved on 1 October 2011.
- ^ BBC (31 July 2012), Peru country profile Archived 5 نوفمبر 2016 at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ "Human Development Reports, Peru". hdr.undp.org (in الإنجليزية). United Nations. 2016. Archived from the original on 28 December 2017. Retrieved 7 January 2018.
- ^ Thorp, p. 4.
- ^ Thorp, p. 321.
- ^ "Overview". Archived from the original on 29 December 2017. Retrieved 2 January 2018.
- ^ "Peru and the IMF". International Monetary Fund. Archived from the original on 3 July 2014. Retrieved 27 July 2014.
- ^ Thorp, pp. 318–319.
- ^ خطأ استشهاد: وسم
<ref>غير صحيح؛ لا نص تم توفيره للمراجع المسماةSheahan - ^ 2006 figures. (in إسپانية) Banco Central de Reserva, Memoria 2006 Archived 9 سبتمبر 2016 at the Wayback Machine, p. 204. Retrieved 27 December 2010.
- ^ (in إسپانية) Banco Central de Reserva, Memoria 2006 Archived 9 سبتمبر 2016 at the Wayback Machine, pp. 15, 203. Retrieved 27 December 2010.
- ^ Office of the U.S. Trade Representative, United States and Peru Sign Trade Promotion Agreement, 12 April 2006. Retrieved 27 December 2010.
- ^ 2006 figures. (in إسپانية) Banco Central de Reserva, Memoria 2006 Archived 9 سبتمبر 2016 at the Wayback Machine, pp. 60–61. Retrieved 27 December 2010.
- ^ "Global Innovation Index 2021". World Intellectual Property Organization (in الإنجليزية). United Nations. Archived from the original on 20 September 2021. Retrieved 2022-03-05.
- ^ USGS Copper Production Statistics Archived 18 أكتوبر 2022 at the Wayback Machine (PDF)
- ^ USGS Silver Production Statistics Archived 15 مايو 2021 at the Wayback Machine (PDF)
- ^ USGS Zinc Production Statistics Archived 15 أكتوبر 2022 at the Wayback Machine (PDF)
- ^ USGS Gold Production Statistics Archived 2 يناير 2020 at the Wayback Machine (PDF) )
- ^ USGS Lead Production Statistics Archived 3 نوفمبر 2022 at the Wayback Machine (PDF)
- ^ USGS Tin Production Statistics Archived 19 أبريل 2022 at the Wayback Machine (PDF)
- ^ USGS Boron Production Statistics Archived 18 يوليو 2021 at the Wayback Machine (PDF)
- ^ USGS Molybdenum Production Statistics Archived 20 مارس 2022 at the Wayback Machine (PDF)
- ^ "Duas opções: direita ou direita". Archived from the original on 12 July 2022. Retrieved 12 July 2022.
- ^ "Agriculture in Peru, by FAO". Archived from the original on 16 October 2020. Retrieved 12 July 2022.
- ^ "Manufacturing, value added (current US$)". Archived from the original on 7 January 2020. Retrieved 12 July 2022.
- ^ "Peru prepara indústria pesqueira". Archived from the original on 12 July 2022. Retrieved 12 July 2022.
- ^ "El Perú tiene una población de 31 millones 488 mil 625 habitantes" [Peru has a population of 31 million 488 thousand 625 inhabitants]. www.inei.gob.pe (in الإسبانية). INEI. 11 July 2016. Archived from the original on 2 February 2017. Retrieved 7 January 2018.
- ^ Instituto Nacional de Estadística e Informática, Perú: Estimaciones y Proyecciones de Población, 1950–2050, pp. 37–38, 40.
- ^ "First results of the Peruvian population census conducted last year". The Peru Telegraph. 26 June 2018. Archived from the original on 10 July 2018. Retrieved 10 July 2018.
- ^ "Perú: Perfil Sociodemográfico" (PDF). Instituto Nacional de Estadística e Informática. p. 16. Archived (PDF) from the original on 11 February 2020. Retrieved 27 September 2018.
- ^ Instituto Nacional de Estadística e Informática, Perfil sociodemográfico del Perú, p. 24.
- ^ "Isolated Peru tribe threatened by outsiders. USAToday.com. 31 January 2012
- ^ "Life expectancy at birth, total (years) | Data". data.worldbank.org (in الإنجليزية الأمريكية). Archived from the original on 26 August 2018. Retrieved 25 August 2018.
- ^ INSTITUTO NACIONAL DE ESTADISTICA E INFORMATICA. "PERÚ: ESTIMACIONES Y PROYECCIONES DE POBLACIÓN TOTAL POR SEXO DE LAS PRINCIPALES CIUDADES" (in الإسبانية). Archived from the original on 16 July 2015. Retrieved 9 December 2021.
- ^ أ ب "Perú: Perfil Sociodemográfico" (PDF). Instituto Nacional de Estadística e Informática. p. 214. Archived (PDF) from the original on 11 February 2020. Retrieved 27 September 2018.
- ^ Cook, Noble David (1982) Demographic collapse: Indian Peru, 1520–1620. Cambridge University Press. p. 114. ISBN 0521239958.
- ^ Vázquez, Mario (1970) "Immigration and mestizaje in nineteenth-century Peru", pp. 79–81 in Race and class in Latin America. Columbia Univ. Press. ISBN 0-231-03295-1
- ^ "Peru apologises for abuse of African-origin citizens Archived 19 يوليو 2018 at the Wayback Machine". BBC News. 29 November 2009
- ^ Mörner, Magnus (1967), Race mixture in the history of Latin America, p. 131.
- ^ "Perú: Perfil Sociodemográfico" (PDF). Instituto Nacional de Estadística e Informática. p. 198. Archived (PDF) from the original on 11 February 2020. Retrieved 27 September 2018.
- ^ أ ب (in إسپانية) Resonancias.org Archived 7 أكتوبر 2016 at the Wayback Machine – Aboriginal languages of Peru
- ^ World University Ranking 2023, Times Higher Education, https://www.times Archived 27 يناير 2022 at the Wayback Machine highereducation.com > world-ranking
- ^ "Catholicism and evangelism: the two most common religions in Latin America". Statista. Archived from the original on 19 November 2022. Retrieved 18 November 2022.
- ^ Instituto Nacional de Estadística e Informática, Perfil sociodemográfico del Perú, p. 93.
- ^ Constitución Política del Perú, Article No. 17.
- ^ "Decreto Supremo que aprueba el Reglamento de la Ley N° 29735, Ley que regula el uso, preservación, desarrollo, recuperación, fomento y difusión de las lenguas originarias del Perú, Decreto Supremo N° 004-2016-MC". Archived from the original on 29 October 2017. Retrieved 10 July 2017.
- ^ خطأ استشهاد: وسم
<ref>غير صحيح؛ لا نص تم توفيره للمراجع المسماةBelaunde - ^ Bailey, pp. 72–74.
- ^ Bailey, p. 263.
- ^ خطأ استشهاد: وسم
<ref>غير صحيح؛ لا نص تم توفيره للمراجع المسماةLucie - ^ Neuman, William (2 January 2016). "Untangling an Accounting Tool and an Ancient Inca Mystery". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 8 January 2016. Retrieved 8 January 2016.
- ^ خطأ استشهاد: وسم
<ref>غير صحيح؛ لا نص تم توفيره للمراجع المسماةBayon - ^ Martin, "Literature, music and the visual arts, c. 1820–1870", pp. 37–39.
- ^ Martin, "Narrative since c. 1920", pp. 151–152.
- ^ Martin, "Narrative since c. 1920", pp. 178–179.
- ^ Martin, "Narrative since c. 1920", pp. 186–188.
- ^ "7 Things You Need to Know about Peruvian Cuisine". MICHELIN Guide. Archived from the original on 4 February 2019. Retrieved 4 February 2019.
- ^ Custer, pp. 17–22.
- ^ Custer, pp. 25–38.
- ^ Romero, Raúl (1999). "Andean Peru". In: John Schechter (ed.), Music in Latin American culture: regional tradition. New York: Schirmer Books, pp. 385–386.
- ^ خطأ استشهاد: وسم
<ref>غير صحيح؛ لا نص تم توفيره للمراجع المسماةOlsen - ^ خطأ استشهاد: وسم
<ref>غير صحيح؛ لا نص تم توفيره للمراجع المسماةTurino - ^ Romero, Raúl (1985). "La música tradicional y popular". In: Patronato Popular y Porvenir, La música en el Perú. Lima: Industrial Gráfica, pp. pp. 243–245, 261–265.
- Short description is different from Wikidata
- Articles containing إسپانية-language text
- Articles containing Quechua-language text
- Articles containing آيمارا-language text
- Pages using gadget WikiMiniAtlas
- Convert errors
- Pages including recorded pronunciations
- Pages using Lang-xx templates
- Pages with plain IPA
- Articles with hatnote templates targeting a nonexistent page
- Vague or ambiguous time from January 2019
- مقالات فيها عبارات متقادمة منذ 2011
- جميع المقالات التي فيها عبارات متقادمة
- All Wikipedia articles needing clarification
- Wikipedia articles needing clarification from July 2019
- مقالات فيها عبارات متقادمة منذ 2014
- مقالات فيها عبارات متقادمة منذ 2012
- مقالات فيها عبارات متقادمة منذ 2010
- مقالات فيها عبارات متقادمة منذ 2017
- Articles with unsourced statements from November 2020
- پيرو
- مستعمرات إسپانية سابقة
- G15 nations
- دول ناطقة بالاسبانية
- CS1 الإسبانية-language sources (es)
- CS1 الإنجليزية الأمريكية-language sources (en-us)
- Articles with إسپانية-language sources (es)