بنكام

بنكام Water clock أو البنكان وفى بلاد الأندلس يسمى البنجانة وهو أسم تراثي قديم (معرب عن الفارسية)أطلق على كل آلة تقوم بضبط الوقت ,أى على أنواع مختلفة من الساعات.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
التاريخ
ذكر حاج خليفة علة البنكامات بقوله:هو علم يعرف به كيفية اتخاذ آلات يقدر بها الزمان وموضوعه حركات مخصوصة في أجسام مخصوصة تنقضي وبقطع مسافات مخصوصة وغايته معرفة أوقات الصلوات وغيرها من غير ملاحظة حركات الكواكب وكذلك معرفة الأوقات المفروضة للقيام بالليل . وانقسمت البنكامات الى الرملية وليس فيها كثير طائل والى بنكامات الماء وهى أصناف ولا ظائل فيها أيضا والى بنكامات دورية معمولة بالدواليب يدير بعضها بعضا.
مصر
بابل
الهند
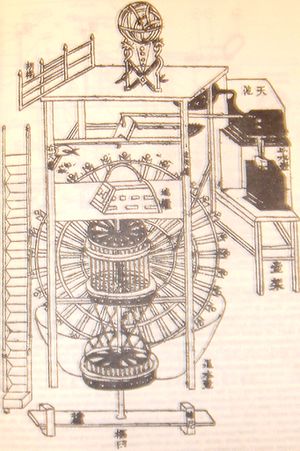
الصين
العالم اليوناني الروماني
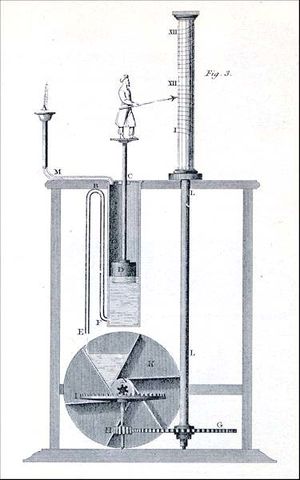
كوريا

العالم العربى والإسلامي
التصاميم الحديثة
المصادر
- مؤمن, عبد الأمير (2006). قاموس دار العلم الفلكي. بيروت، لبنان: دار العلم للملايين.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|طبعة أولى coauthors=(help)
ملاحظات
|
بيلوگرافيا
- استعراض عام للساعات المائية وأجهزة قياس الزمن الأخرى
- Barnett, Jo Ellen. Time's Pendulum: From Sundials to Atomic Clocks, the Fascinating History of Timekeeping and How Our Discoveries Changed the World. Plenum Press, NY, 1998. ISBN 0-15-600649-9
- Bruton, Eric. The History of Clocks and Watches. 1979. ISBN 0-8478-0261-2
- Cowan, Harrison J. (1958). "Time and Its Measurement: From the stone age to the nuclear age". Ohio: The World Publishing Company.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - Dohrn-van Rossum, Gerhard (1996). History of the Hour: Clocks and Modern Temporal Orders. Trans. Thomas Dunlap. The University of Chicago Press. ISBN 0226155102. OCLC 33440282.
- K. Higgins, D. Miner, C.N. Smith, D.B. Sullivan (2004), A Walk Through Time (version 1.2.1). [Online] Available: http://physics.nist.gov/time [2005, December 8]. National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg, MD.
- Jespersen, James and Fitz-Randolph, Jane. "From Sundials to Atomic Clocks: Understanding Time and Frequency." Second Revised Edition, 1999. ISBN 0-486-40913-9
- King, David A. “Towards a History from Antiquity to the Renaissance of Sundials and Other Instruments for Reckoning Time by the Sun and Stars.” Annals of Science, Taylor & Francis. V. 61, Num. 3. July 2004. pp. 375-388. DOI: 10.1080/00033790310001642795.
- Landes, D. Revolution in Time. Harvard University Press (1983).
- McNown, J.S. “When Time Flowed: The Story of the Clepsydra.” La Houille Blanche, 5, 1976, 347-353. ISSN 0018-6368
- Milham, Willis I. Time & Timekeepers including The History, Construction, Care, and Accuracy of Clocks and Watches. The Macmillan Company, NY 1945.
- Rees, Abraham. “Rees's Clocks, Watches, and Chronometers 1819-20.” Charles E. Tuttle Company, Inc. 1970.
- Richards, E.G. "Mapping Time: The Calendar and Its History." Oxford University Press, 1998.
- Toulmin, Stephen & Goodhead, J. The Discovery of Time. University of Chicago Press, 1999. ISBN 0-226-80842-4
- Turner, Anthony J. (1984). The Time Museum. Vol. I: Time Measuring Instruments, Part 3: Water-clocks, Sand-glasses, Fire-clocks. Rockford, IL: The Museum. ISBN 0-912947-01-2. OCLC 159866762.
{{cite book}}: More than one of|location=and|place=specified (help)
- الساعات المائية العربية والإسلامية
- Hill, Donald Routledge (ed. & trans.) (1976). Archimedes “On the Construction of Water-Clocks,” Turner & Devereux, Paris.
- Hill, D.R. (1981). "Arabic Water - Clocks". Syria: University of Aleppo.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - al-Hassan, Ahmad Y.; Hill, Donald R. (1986). Islamic Technology: An Illustrated History. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521263336. OCLC 13332728.
- Hill, Donald Routledge. “Studies in Medieval Islamic Technology: From Philo to Al-Jazari - from Alexandria to Diyar Bakr.” (Collected Studies Series, 555)
- King, D. Mikat. “Astronomical Timekeeping.” The Encyclopaedia of Islam. 7, Brill, (1990) Reprinted as Chapter V in King, D. “Astronomy in the Service of Islam Variorum.” (1993)
- الساعات المائية البابلية
- Englund, R.K. "Administrative Timekeeping in Ancient Mesopotamia." Journal of the Economic and Social History of the Orient, V. XXXI, 31 (1988) 121-185.
- Fermor, John, & Steele, John M. “The design of Babylonian waterclocks: Astronomical and experimental evidence.” Centaurus. International Journal of the History of Mathematics, Science, and Technology. Vol. 42 Issue 3, pp. 210-222. July 2000. Blackwell Publishing.
- Hّyrup, J., “A Note on Waterclocks and the Authority of Texts.” Archiv für Orientforschung, 44/45 (1997/98), 192-194 (*).
- Michel-Nozières, C. “Second Millennium Babylonian Water Clocks: a physical study.” Centaurus, Vol. 42, Issue 3, pp. 180-209. July 2000.
- Neugebauer, Otto (1947). "Studies in Ancient Astronomy. VIII. The Water Clock in Babylonian Astronomy". Isis. 37 (1/2): 37–43. doi:10.1086/347965.. JSTOR link. Reprinted in Neugebauer (1983), pp. 239-245 (*).
- Price, Derek deSolla. Science Since Babylon. Yale University Press, New Haven 1976.
- Teresi, Dick. "Lost Discoveries: The Ancient Roots of Modern Science - from the Babylonians to the Maya." Simon & Schuster, NY 2002.
- van der Waerden, Bartel Leendert, “Babylonian Astronomy: III. The Earliest Astronomical Computations.” Journal of Near Eastern Studies, 10 (1951), 20-34 JSTOR link.
- Chinese water clocks
- Lorch, Richard P. "Al-Khazini's Balance-clock and the Chinese Steelyard Clepsydra." Archives Internationales d'Histoire des Sciences, June 1981, 31: 183-189.
- Needham, J., Ling, W., and de Solla Price, D.J. "Heavenly Clockwork: The Great Astronomical Clocks of Medieval China." 2nd Edition. 1986. ISBN 0-521-32276-6.
- Needham, Joseph (1995). Science & Civilisation in China. Vol. III: Mathematics and the Sciences of the Heavens and the Earth. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521058015. OCLC 153247126.
- Needham, Joseph (2000). Science & Civilisation in China. Vol. IV:2: Mechanical Engineering. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521058031. OCLC 153247141.
- Quan, He Jun. “Research on scale and precision of the water clock in ancient China.” History of Oriental Astronomy, pp. 57-61. (Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union Colloquium No. 91 held in New Delhi, November 13-16, 1985). Edited by G. Swarup, A. K. Bag and K. S. Shukla. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1987. ISBN 0-521-34659-2.
- Walsh, Jennifer Robin. “Ancient Chinese Astronomical Technologies.” American Physical Society, Northwest Section. May, 2004. Meeting, 21-22 May, 2004. Pullman, WA.
- Egyptian water clocks
- Clagett, Marshall. Ancient Egyptian Science, Volume II: Calendars, Clocks, and Astronomy. 1995. pp. 457-462. ISBN 0-87169-214-7
- Cotterell, B., Dickson, F.P., and Kamminga, J. “Ancient Egyptian Water-clocks: A Reappraisal.” Journal of Archaeological Science. Vol. 13, pp. 31-50. 1986.
- Cotterell, Brian and Kamminga, Johan. “Mechanics of pre-industrial technology.” Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. 1990.
- Fermor, John, “Timing the Sun in Egypt and Mesopotamia.” Vistas in Astronomy, 41 (1997), pp. 157-167. Elsevier Science. DOI: 10.1016/S0083-6656(96)00069-4.
- Neugebauer, Otto & Parker, Richard A. “Egyptian Astronomical Texts: Iii. Decans, Planets, Constellations, and Zodiacs.”
- Pogo, Alexander. “Egyptian water clocks”, Isis, vol. 25, pp. 403-425, 1936. Reprinted in Philosophers and Machines, O. Mayr, editor, Science History Publications, 1976. ISSN 0021-1753
- Sloley, R.W., "Ancient Clepsydrae", Ancient Egypt, 1924, pp. 43-50.
- Sloley, R.W., "Primitive methods of measuring time", JEA 17, 1931, pp. 174-176.
- European water clocks
- Bedini, S.A. "The Compartmented Cylindrical Clepsydra." Technology and Culture 3(2):115-141. 1962. ISSN 0040-165X
- Drover, C.B. "A Medieval Monastic Water Clock", Antiquarian Horology, Vol. I, No. 5 (1954), pp. 54-58.
- Hill, Donald Routledge. "A History of Engineering in Classical and Medieval Times." La Salle, Ill., Open Court Pub. 1996. ISBN 0-415-15291-7
- Hill, D.R. "The Toledo Water-Clocks of c.1075." History of Technology, vol.16, 1994, pp. 62-71
- Scattergood, John. "Writing the clock: the reconstruction of time in the late Middle Ages." European Review, Issue 4 (Oct, 2003), 11: pp. 453-474 Cambridge University Press (School of English, Trinity College, Dublin 2, Ireland. jscatter@tcd.ie)
- Greek and Alexandrian water clocks
- Hill, D.R. (ed. & trans.) (1976). Archimedes “On the Construction of Water-Clocks,” Turner & Devereux, Paris.
- Lepschy, Antonio M. "Feedback Control in Ancient Water and Mechanical Clocks." IEEE Transactions on Education, Vol. 35, No. 1, February, 1992.
- Lewis, Michael (2000), "Theoretical Hydraulics, Automata, and Water Clocks", in Wikander, ضrjan, Handbook of Ancient Water Technology, Technology and Change in History, 2, Leiden, pp. 343–369 (356f.), ISBN 90-04-11123-9
- Noble, J.V. & de Solla Price, D. J. “The Water clock in the Tower of the Winds.” American Journal of Archaeology, 72, 1968, pp. 345-355.
- Woodcroft, Bennet (translator). "The Pneumatics of Hero of Alexandria." London, Taylor Walton and Maberly, 1851.
- Vitruvius, P., The Ten Books on Architecture. (M.H. Morgan, translator) New York: Dover Publications, Inc., 1960.
- Indian water clocks
- Achar, N. “On the Vedic origin of the ancient mathematical astronomy of India.” Journal of Studies on Ancient India, vol 1, 95-108, 1998.
- Fleet, J. F., “The ancient Indian water clock.” Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society, 213-230, 1915.
- Kumar, Narendra "Science in Ancient India" (2004). ISBN 8126120568.
- Pingree, D. “The Mesopotamian origin of early Indian mathematical astronomy.” Journal of the History of Astronomy, vol. 4, 1-12, 1973.
- Pingree, D. “The recovery of early Greek astronomy from India.” Journal for the History of Astronomy, vol 7, 109-123, 1976.
- Japanese water clocks
- Kiyoyasu, Maruyma. "Hoken shakai to gijutsu - wadokei ni shuyaku sareta hoken gijutsu." Kagakushi kenkyu, Sept. 1954, 31:16-22.
- Korean water clocks
- Hahn, Young-Ho and Nam, Moon-Hyon. "Reconstruction of the Armillary Spheres of Mid-Chosun: The Armillary Clocks of Yi Minchol." Hanguk Kwahaksa Hakhoeji (Journal of the Korean History of Science Society)19.1 (1997): 3-19. (in Korean)
- Hahn, Young-Ho, et al. "Astronomical Clocks of Chosun Dynasty: King Sejong's Heumgyonggaknu. Kisulgwa Yoksa (Journal of the Korean Society for the History of Technology and Industry) 1.1 (2000): 99-140. (in Korean).
- Hong, Sungook "Book Review: Korean Water-Clocks: "Chagyongnu", the Striking Clepsydra, and the History of Control and Instrumentation Engineering." Technology and Culture - Volume 39, Number 3, July 1998, pp. 553-555
- Nam, Moon-Hyon. “Chagyongnu: The Automatic Striking Water clock.” Korea Journal, 30.7 (1990): 9-21.
- Nam, Moon-Hyon. Korean Water Clocks: Jagyongnu, The Striking Clepsydra and The History of Control and Instrumentation Engineering. Seoul: Konkuk University Press, 1995. (in Korean)
- Nam, Moon-Hyon. On the BORUGAKGI of Kim Don -- Principles and Structures of JAYEONGNU. Hanguksa Yeongu (Studies on Korean History),101 (1998): 75-114 (in Korean)
- Nam, Moon-Hyon. Jang Yeong-Shil and Jagyeongnu - Reconstruction of Time Measuring History of Choseon Period. Seoul National University Press, 2002. (in Korean)
- Nam, Moon-Hyon and Jeon San-Woon. “Timekeeping Systems of Early Choson Dynasty.” Proceedings of First International Conference on Oriental Astronomy, From Guo Shoujing to King Sejong, Seoul, October 6-11, 1993, Seoul, Yonsei University Press, 1997. 305-324.
- Needham, Joseph, Major, John S., & Gwei-Djen, Lu. “Hall of Heavenly Records: Korean Astronomical Instruments and Clocks, 1380-1780.” Cambridge [Cambridgeshire] ; New York : Cambridge University Press, 1986. ISBN 0-521-30368-0
- Hyeonjong Shillock (Veritable Records of King Hyeonjong), 1669
- Jungjong Shillok (Veritable Records of King Jungjong), 1536.
- Sejong Shillock (Veritable Records of King Sejong), Chapter. 65, A.D. 1434 and Chapter. 80, A.D. 1438.
- Mesopotamian water clocks
- Brown, David R., Fermor, John, & Walker, Christopher B.F., “The Water Clock in Mesopotamia.” Archiv für Orientforschung, 46/47 (1999/2000)
- Chadwick, R. “The Origins of Astronomy and Astrology in Mesopotamia.” Archaeoastronomy. BULL. CTR ARCH. V. 7:1-4, P. 89, 1984. KNUDSEN Bibliographic Code: 1984BuCAr...7...89C
- Fermor, John, “Timing the Sun in Egypt and Mesopotamia.” Vistas in Astronomy, 41 (1997), 157-167. Elsevier Science. DOI: 10.1016/S0083-6656(96)00069-4.
- Walker, Christopher and Britton, John. “Astronomy and Astrology in Mesopotamia.” BMP, 1996 (especially pp. 42-67)
- Present-day water clocks
- Gitton, Bernard. “Time, like an everflowing stream.” Trans. Mlle. Annie Chadeyron. Ed. Anthony Randall. Horological Journal 131.12 (June 1989): 18-20.
- Taylor, Robert. "Taiwan's Biggest Cuckoo Clock?: Recreating an Astronomical Timepiece". Sinorama Magazine. 3-15-2006
- Xuan, Gao. "Principle Research and Reconstruction Experiment of the Astronomical Clock Tower in Ancient China." Proceeding of the 11th World Congress in Mechanism and machine Science. August 18-21, 2003. Tianjin, China.
- Other topics on water clocks and related material
- Goodenow, J., Orr, R., & Ross, D. "Mathematical Models of Water Clocks." Rochester Institute of Technology
- Landels, John G. "Water-Clocks and Time Measurement in Classical Antiquity." Endeavour 3(1):32-37. 1979. ISSN 0160-9327
- Mills, A.A. “Newton’s Water Clocks and the Fluid Mechanics of Clepsydrae.” Notes and Records of the Royal Society of London. 37(1):35-61. 1982. ISSN 0035-9149
- Neugebauer, Otto. The Exact Sciences in Antiquity. Dover Publications, NY 1969.
- Sarma, S.R., “Setting up the Water Clock for Telling the Time of Marriage.” in Studies in the History of the Exact Sciences in Honour of David Pingree, éd. Ch. Burnett, J.P. Hogendijk, K. Plofker, M. Yano, Leiden-Boston, 2004, pp. 302-330.
- Snell, Daniel. “Life in the Ancient Near East, 3100-332 B.C.E.” ISBN 0-300-07666-5.
- Non-English resources
- Bilfinger, Gustav, Die babylonische Doppelstunde: Eine chronologische Untersuchung (Wildt, Stuttgart, 1888).
- Borchardt, Ludwig. 1920. “Die Altنgyptische Zeitmessung.” (Old Egyptian time measurement). Berlin/Leipzig.
- Daressy, G., "Deux clepsydres antiques", BIE, serie 5, 9, 1915, pages 5-16
- Ginzel, Friedrich Karl, “Die Wassermessungen der Babylonier und das Sexagesimalsystem”, Klio: Beitrنge zur alten Geschichte, 16 (1920), 234-241.
- Planchon, "L'Heure Par Les Clepsydres." La Nature. pp.55-59.
- Thureau-Dangin, François, “La clepsydre chez les Babyloniens [Notes assyriologiques LXIX]”, Revue d’assyriologie et d’archéologie orientale, 29 (1932), 133-136.
- Thureau-Dangin, François, “Clepsydre babylonienne et clepsydre égyptienne”, Revue d’assyriologie et d’archéologie orientale, 30 (1933), 51-52.
- Thureau-Dangin, François, “Le clepsydre babylonienne”, Revue d’assyriologie et d’archéologie orientale, 34 (1937), 144.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
أنظر ايضا
وصلات خارجية
| Water clocks
]].- NIST: A Walk Through Time
- Egypt's Water Clock
- A Brief History of Clocks: From Thales to Ptolemy
- The Indianapolis Children's Museum Water Clock
- Nanaimo, BC Water Clock
- Rees's Universal Dictionary article on Clepsydra, 1819
- Bernard Gitton's Time-Flow Clocks
- The Royal Gorge Bridge Water Clock
- Shockwave-Applet: Ctesibius Waterclock