ملايو (شعب)
(تم التحويل من Malays (ethnic group))
 زوجان من الملايو في حفل زواج تقليدي. | |
| المناطق ذات التجمعات المعتبرة | |
|---|---|
| المنطقة الأصلية | . |
| 5,365,399[3] | |
| 1,964,384[4] | |
| 653,449[5] | |
| ~27,000[6] | |
| الشتات | . |
| ~200,000[7][1] | |
| 40,189[8][2] | |
| 33,183[9] | |
| ~33,000[10] | |
| اللغات | |
| Official:
اللهجات: Others:
| |
| الدين | |
^ note: Highly naturalised population of mixed origins, but using the 'Malay' identity | |
الملايو (ملايو: Orang Melayu، بالجاوية: أورڠ ملايو)، هي جماعة عرقية من الشعوب الأسترونسية والتي تستوطن شبه جزيرة الملايو، شرق سومطرة وبرونيو الساحلية، وكذلك بعض الجزر الأصغر والتي تقع بين هذه المواقع-المناطق التي تعرف مجتمعة بعالم الملايو. هذه المناطق تعتبر اليوم جزءاً من دول ماليزيا، أستراليا، إندونسيا، بروناي، سنغافورة، وجنوب تايلاند.
التسمية

Joget dance from the Malacca Sultanate; many aspects of Malay culture are derived from the Malaccan court.
الأصول
أنماط ما قبل الملايو
التاريخ
النفوذ الهندوسي :
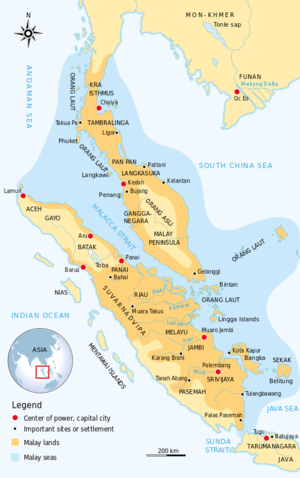
Early Malayic and pre-Malayic-speaking areas, classical kingdoms and urban settlements preceding the rise of Srivijaya in the 7th century and prior to the eastward Malay cultural expansion to the shores of Borneo. It also can be witnessed that the historical forebears of Minangkabaus, eastern Acehnese and Southern Thais were of Malay origin during this era.

Chedi Phra Borommathat, a stupa located in Nakhon Si Thammarat, تايلند. Once a centre of Buddhist teaching and learning, it was built in the early 13th century and witnessed the rise and fall of Tambralinga, a powerful Buddhist-Malay kingdom that managed to conquer Jaffna kingdom in Sri Lanka. Constructed as a religious monument for Mahayana Buddhism, which was historically followed by a portion of pre-Islamic Malays, this stupa stands today as a major religious site for Thai, Theravada Buddhist pilgrims. The temple complex is believed to hold ancient relics of Buddha brought from Sri Lanka during the conquest of Jaffna in 1247.
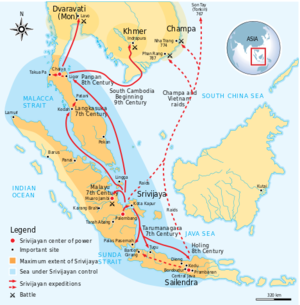
The Buddhist maritime empire of Srivijaya, the first vast Malay polity in the region
دخول الإسلام
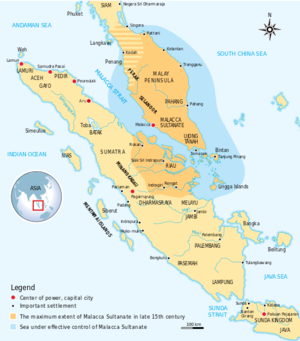
The extent of the Malaccan Sultanate in the 15th century. This was a powerful empire that has effectively molded the Malay-Muslim socio-cultural identity until this day.

The reigning elite of the Riau-Lingga Sultanate, together with the Sultan (being seated, in the middle) as depicted in this photograph taken in 1867. The administrative class of Riau-Lingga are known to be strict adherents of Sufi Tariqa, this resulted various laws and legal enactments based on Islamic principles to be strictly observed throughout the kingdom. The sultanate would be abolished under the Dutch powers in almost half a century after the image was taken, in 1911
الاستعمار

Tuan Lebeh Long Raya (seated, in the middle) in 1899, the Raja Muda (crown prince) of the Reman Sultanate. A kingdom in the northern Malay Peninsula made wealthy by tin mining, the State of Reman was abolished by the Rattanakosin Kingdom alongside various other Malay kingdoms that revolted for independence in the early 20th century including Pattani, Saiburi, Nongchik, Yaring, Yala, Legeh and Teluban.
القومية الملاوية

The bronze mural of the legendary Malay warrior, Hang Tuah with his renowned quote Ta' Melayu Hilang Di-Dunia (Malay for "Never shall the Malays vanish from the face of the earth") written on the top. The quote is a famous rallying cry for Malay nationalism.[11][12]
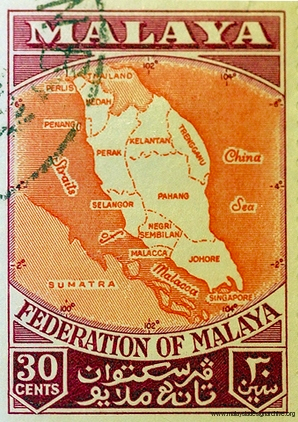
Federation of Malaya's commemorative stamp issued in 1957. The semi-independent federation was formed in 1948 from nine Malay states and two British Straits Settlements. It achieved independence in 1957.

Supporters of Negara Soematra Timoer (State of East Sumatra) that sought to maintain the monarchy system in post-World War II Dutch-established territory of East Sumatra. The state was headed by a president, Dr. Tengku Mansur, a member of Asahan royal family. Both the state and the traditional Malay monarchy institution in East Sumatra dissolved following her merger into the newly formed unitarian Republic of Indonesia in 1950. (image taken c. 1947–1950)
الثقافة
اللغة

The Kedukan Bukit Inscription written in Pallava script. Dating back from 683, it is one of the oldest surviving Malay written artefact.
الأدب

Hikayat Merong Mahawangsa in Jawi text. Also known as the Kedah Annals, it is an ancient Malay literature that chronicles the bloodline of Merong Mahawangsa and the foundation of Kedah.
الديانة

Sultan Omar Ali Saifuddin Mosque in Brunei on the eve of Ramadhan. The wealthy kingdom adopted Melayu Islam Beraja (Malay Islamic Monarchy) as the national philosophy since its independence in 1984.
العمارة

The replica of Malacca Sultanate's palace which was built from information and data obtained from the Malay Annals. This historical document had references to the construction and the architecture of palaces during the era of Sultan Mansur Shah, who ruled from 1458 to 1477.
الفنون البصرية
المطبخ
الفنون التطبيقية

A troupe of Siamese Malay dancers performing the Mak Yong during the reign of King Rama V of Siam (c. 19th century), a dance theatre that owes its origin from the Pattani and Kelantanese palace courts. In 2005, it received recognition as being among the masterpieces of the oral and intangible heritage of humanity by UNESCO.
الزي التقليدي

أطفال ملاويون يرتدون الزي التقليدي أثناء عيد الفطر.
الفنون القتالية
الألعاب التقليدية

A close-up to two Malay style Gasings.
الأسماء والألقاب
الجماعات العرقية الفرعية
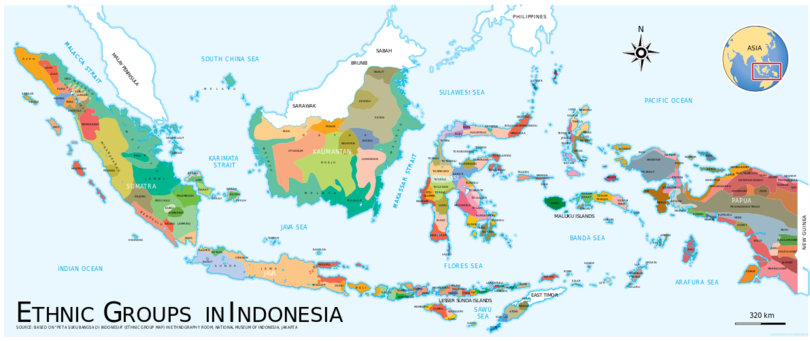
Ethnic Malays among other ethnic groups in Indonesia. Although only constituting 3.4% of total population, ethnic Malays are one of the most widely distributed ethnicities in Indonesia. The realm of Malays is described in green and other related sub-ethnic groups are rendered in darker or lighter green. Malay ethnic groups are depicted to inhabit eastern coast of Sumatra and coastal Kalimantan. Outside the Indonesian Archipelago in white, the Malay people inhabit the Malay Peninsular, forming the dominant ethnic group in Peninsular Malaysia and significant minority in Singapore, Thailand and southern Myanmar. While the eastern core of Bornean Malay territories beginning north from southwestern Sabah, Brunei, coastal Sarawak and continuing down to the green shaded shores of Kalimantan.[13]
هذه القائمة غير مكتملة؛ بإمكانك المساعدة بتنميتها.
انظر أيضاً
- مناهضة العرقية الملاوية، تعصب عرقي ضد العرقية الملاوية
- Ketuanan Melayu (تفوق ملاوي)
- قائمة الملاويين
- فلكلور ملاوي
- الشبح في الثقافة الملاوية
- ملكية إسلامية ملاوية، الفلسفة القومية of Negara Brunei Darussalam
- وحدات القياس الملاوية
المصادر
- ^ Economic Planning Unit (Malaysia) 2010
- ^ خطأ استشهاد: وسم
<ref>غير صحيح؛ لا نص تم توفيره للمراجع المسماةCIA (B) - ^ Badan Pusat Statistika Indonesia 2010, p. 9
- ^ World Population Review 2015
- ^ CIA World Factbook 2012
- ^ Malay in Myanmar - Joshua Project
- ^ Malay, Cape in South Africa - Joshua Project
- ^ Department of Census and Statistics, Sri Lanka - Population by ethnic group according to districts, 2012
- ^ Australia - Ancestry
- ^ Malay in United Kingdom - Joshua Project
- ^ Tan 1988, p. 14
- ^ Chew 1999, p. 78
- ^ In search of Brunei Malays outside Brunei
- ^ Umaiyah Haji Omar 2003
- ^ Umaiyah Haji Omar 2007
- ^ IBP USA 2007, pp. 151–152
- ^ أ ب ت ث ج ح خ د ذ Colling 1973, p. 6804
- ^ أ ب ت ث ج ح خ د ذ Mohd. Aris Hj. Othman 1983, pp. 1–26
- ^ أ ب ت ث ج ح خ د ذ M. G. Husain 2007, pp. 16, 33, 34
- ^ أ ب ت Gulrose Karim 1990, p. 74
- ^ أ ب ت Joseph & Najmabadi 2006, p. 436
- ^ "Mempawah Sultanate<". Melaju Online.
- ^ Majlis Kebudayaan Negeri Kedah 1986, pp. 19–69
- ^ "Setoi (Setul) Mambang Segara Dalam Lintasan Sejarah Negeri-Negeri Melayu Utara". Jurnal Perspektif Jil. 8 Bil. 2(123-134).
- ^ Nik Anuar 1999, p. 39
- ^ Nik Anuar 1999, p. 39
- ^ Nik Anuar 1999, p. 39
- ^ Nik Anuar 1999, p. 39
- ^ Nik Anuar 1999, p. 39
المراجع
- A. Ghafar Ahmad, Malay Vernacular Architecture, Archived from the original on 10 June 2010, https://web.archive.org/web/20100610190114/http://www.hbp.usm.my/conservation/malayvernacular.htm, retrieved on 24 June 2010
- Abd. Rahman Ismail (2008), Seni Silat Melayu: Sejarah, Perkembangan dan Budaya, Kuala Lumpur: Dewan Bahasa dan Pustaka, ISBN 978-983-62-9934-5
- Abdul Rashid Melebek; Amat Juhari Moain (2006), Sejarah Bahasa Melayu ("History of the Malay Language"), Utusan Publications & Distributors, ISBN 967-61-1809-5
- Abu Talib Ahmad; Tan, Liok Ee (2003), New terrains in Southeast Asian history, Singapore: Ohio University press, ISBN 9971-69-269-4
- Ahir, Diwan Chand (1995), A Panorama of Indian Buddhism: Selections from the Maha Bodhi journal, 1892–1992, Sri Satguru Publications, ISBN 81-7030-462-8
- Ahmad Salehuddin (2009), Serampang dua belas, Tari Tradisional Kesultanan Serdang, http://asalehudin.wordpress.com/2009/04/25/serampang-duabelas-tari-tradisional-melayu-kesultanan-serdang-sumatra-utara/, retrieved on 15 June 2012
- Alexander, James (2006), Malaysia Brunei & Singapore, New Holland Publishers, ISBN 978-1-86011-309-3
- Ananta, Aris (2013). "Changing Ethnic Composition:Indonesia, 2000–2010"., Busan, Korea: International Union for the Scientific Study of Population.
- Andaya, Barbara Watson; Andaya, Leonard Yuzon (1984), A History of Malaysia, London: Palgrave Macmillan, ISBN 0-333-27672-8
- Badan Pusat Statistika Indonesia (2010), Hasil Sensus Penduduk 2010 - Kewarganegaraan, Suku Bangsa, Agama dan Bahasa sehari-hari penduduk Indonesia, http://demografi.bps.go.id/phpfiletree/bahan/kumpulan_tugas_mobilitas_pak_chotib/Kelompok_1/Referensi/BPS_kewarganegaraan_sukubangsa_agama_bahasa_2010.pdf
- Barnard, Timothy P. (2004), Contesting Malayness: Malay identity across boundaries, Singapore: Singapore University press, ISBN 9971-69-279-1
- Barrington, Lowell (2006), After Independence: Making and Protecting the Nation in Postcolonial and Postcommunist States, University of Michigan Press, ISBN 978-0-472-06898-2
- BBC News (11 December 2009), Genetic 'map' of Asia's diversity, http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/8406506.stm
- Bethany World Prayer Center (1997), The Malay of Malaysia, Archived from the original on 10 October 2012, https://web.archive.org/web/20121010191042/http://kcm.co.kr/bethany_eng/p_code3/1892.html, retrieved on 28 February 2014
- Bethany World Prayer Center (1997), The Diaspora Malay, Archived from the original on 18 July 2012, https://web.archive.org/web/20120718130911/http://kcm.co.kr/bethany_eng/clusters/8101.html, retrieved on 28 February 2014
- Bolton, Kingsley; Hutton, Christopher (2000), Triad societies: western accounts of the history, sociology and linguistics of Chinese secret societies, 5, London: Routledge, ISBN 0-415-24397-1
- Boyd, Kelly (1999), Encyclopedia of historians and historical writing, 2, London: Fitzroy Darborn Publishers, ISBN 1-884964-33-8
- Brown, Keith; Ogilvie, Sarah (2009), Concise encyclopedia of languages of the world, Elsevier Science, ISBN 978-0-08-087774-7
- Burgat, François (2003), Face to face with political Islam (L'islamisme en face), New York: I.B Tauris & Co. Ltd, ISBN 1-86064-212-8
- Buyers, Christopher (2008), The Ruling House of Malacca – Johor, http://www.royalark.net/Malaysia/malacca.htm
- Chew, Melanie (1999), The Presidential Notes: A biography of President Yusof bin Ishak, Singapore: SNP Publications, ISBN 978-981-4032-48-3
- Chihara, Daigorō (1996), Hindu-Buddhist architecture in Southeast Asia, BRILL, ISBN 90-04-10512-3
- CIA World Factbook (2012), Brunei, https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/bx.html, retrieved on 28 February 2014
- CIA World Factbook (2012), Singapore, https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/sn.html, retrieved on 28 February 2014
- Clyne, Michael G. (1992), Pluricentric languages: differing norms in different nations, De Gruyter Mouton, ISBN 978-3-11-012855-0
- COAC (2006), Orang Asli Population Statistics, http://www.coac.org.my/codenavia/portals/coacv2/code/main/main_art.php?parentID=11374494101180&artID=11432750280711
- Colling, Patricia (1973), Dissertation Abstracts International, A-The Humanities and Social Sciences (Abstracts of Dissertations Available on Microfilm or as Xerographic Reproductions February 1973), 33, #8, New York: Xerox University Microfilms, ISSN 0419-4209
- Collins, Alan (2003), Security and Southeast Asia: domestic, regional, and global issues, Singapore: Institute of Southeast Asian Studies, ISBN 981-230-230-1
- Cordier, Henri (2009), Ser Marco Polo; notes and addenda to Sir Henry Yule's edition, containing the results of recent research and discovery, Bibliolife, ISBN 978-1-110-77685-6
- Deka, Phani (2007), The great Indian corridor in the east, Mittal Publications, ISBN 81-8324-179-4
- Devan, Subhadra (2010), New interest in an older Lembah Bujang, NST, http://www.usm.my/index.php/about-usm/news-archive/67-papercutting-/7078-New-interest-in-an-older-Lembah-Bujang-.html
- Dewaele, Jean-Marc; Beardsmore, Hugo Baetens; Housen, Alex; Li, Wei (2003), Bilingualism: beyond basic principles, Multilingual Matters, ISBN 978-1-85359-625-4
- Draeger, Donn F. (1992), Weapons and fighting arts of Indonesia, Tuttle Publishing, ISBN 0-8048-1716-2
- Economic Planning Unit (Malaysia) (2010), Population by sex, ethnic group and age, Malaysia,2010, http://www.epu.gov.my/html/themes/epu/images/common/pdf/eco_stat/pdf/1.2.5.pdf
- Esposito, John L. (1999), The Oxford History of Islam, New York: Oxford University Press, ISBN 978-0-19-510799-9, https://books.google.com/books?id=9HUDXkJIE3EC&pg=PT841
- Europa Publications Staff (2002), Far East and Australasia (34th edition), Routledge, ISBN 978-1-85743-133-9
- Farish Ahmad Noor; Khoo, Eddin (2003), Spirit of wood: the art of Malay woodcarving : works by master carvers from Kelantan, Terengganu, and Pattani, Singapore: Periplus Editions (HK) Ltd., ISBN 0-7946-0103-0
- Farrer, D. S. (2009), Shadows of the Prophet: Martial Arts and Sufi Mysticism, Springer, ISBN 978-1-4020-9355-5
- Ford, R. Clyde (1899), "Malay Literature", Popular Science Monthly 55
- Ganguly, Šumit (1997), Government Policies and Ethnic Relations in Asia and the Pacific, MIT press, ISBN 978-0-262-52245-8
- Gerini, Gerolamo Emilio (1974), Researches on Ptolemy's geography of eastern Asia (further India and Indo-Malay archipelago, Oriental Books Reprint Corporation, ISBN 81-7069-036-6
- Ghulam Sarwar Yousof (1997), The Malay Shadow Play: An Introduction, The Asian Centre, ISBN 983-9499-02-5
- Gopal, Lallanji (2000), The economic life of northern India: c. A.D. 700–1200, Motilal Banarsidass, ISBN 978-81-208-0302-2
- Guoxue (2003), Chronicle of Mongol Yuan, http://www.guoxue.com/shibu/24shi/yuanshi/yuas_210.htm
- Green, Thomas A. (2001), Martial arts of the world: An Encyclopedia., Santa Barbara: ABC-CLIO Inc, ISBN 1-57607-150-2
- Gulrose Karim, Information Malaysia 1990–91 Yearbook (1990), Muslim identity and Islam: misinterpreted in the contemporary world, Kuala Lumpur: Berita Publishing Sdn. Bhd, ISBN 81-7827-165-6
- Hall, Daniel George Edward (1981), History of South East Asia, Macmillan, ISBN 978-0-333-24163-9
- Harper, Timothy Norman (2001), The End of Empire and the Making of Malaya, London: Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-00465-7, https://books.google.com/books?id=lmazmo6_RYMC
- Hatin, WI; Nur-Shafawati, AR; Zahri, M-K; Xu, S; Jin, L (2011), "Population Genetic Structure of Peninsular Malaysia Malay Sub-Ethnic Groups" in PLoS ONE 6(4): e18312. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0018312
- He, Baogang; Galligan, Brian; Inoguchi, Takashi (2007), Federalism in Asia, London: Edward Elgar Publications, ISBN 978-1-84720-140-9
- Hunter, William Wilson; Roberts, Paul Ernest (2010), A History of British India: To the Overthrow of the English in the Spice Archipelago, Nabu Press, ISBN 978-1-145-70716-0
- Hussin Mutalib (2008), Islam in Southeast Asia, Singapore: Institute of Southeast Asian Studies, ISBN 978-981-230-758-3
- I Ching (2005), Takakusu, Junjiro, ed., A Record of the Buddhist Religion As Practised in India and the Malay Archipelago (A.D. 671–695), Asian Educational Services, ISBN 978-81-206-1622-6
- IBP USA (2007), Brunei Sultan Haji Hassanal Bolkiah Mu'izzaddin Waddaulah Handbook (World Strategic and Business Information Library, International Business Publications, ISBN 978-1-4330-0444-5
- Ismail Said (2005), Criteria for Selecting Timber Species in Malay Woodcarving, University Teknologi Malaysia, http://fabserver.utm.my/download/ConferenceSemiar/SelectingTimber.pdf, retrieved on 15 January 2011
- Ismail Said (2002), Visual Composition of Malay Woodcarvings in Vernacular House of Peninsular Malaysia, University Teknologi Malaysia, http://eprints.utm.my/1421/1/JT37B4.pdf, retrieved on 15 January 2011
- James, Michael (1994), Black Belt, Rainbow Publications, ISSN 0277-3066
- Jamil Abu Bakar (2002), A design guide of public parks in Malaysia, Kuala Lumpur: Penerbit UTM, ISBN 983-52-0274-5
- Jan Henket, Hubert; Heynen, Hilde (2002), Back from utopia: the challenge of the modern movement, Rotterdam: 010 Publishers, ISBN 90-6450-483-0
- Jermsawatdi, Promsak (1989), Thai art with Indian influences, Abhinav Publications, ISBN 81-7017-090-7
- Johan Jaaffar; Safian Hussain; Mohd Thani Ahmad (1992), History of Modern Malay Literature, Kuala Lumpur: Dewan Bahasa dan Pustaka & Ministry of Education (Malaysia), ISBN 983-62-2745-8
- Johns, Anthony Hearle; Lahoud, Nelly (2005), Islam in world politics, New York: Routledge, ISBN 0-415-32411-4
- Joseph, Suad; Najmabadi, Afsaneh (2006), Economics, Education, Mobility And Space (Encyclopedia of women & Islamic cultures), Brill Academic Publishers, ISBN 978-90-04-12820-0
- Kementerian Kebudayaan; Belia dan Sukan (2009), Pakaian Tradisi, Pelita Brunei, Archived from the original on 4 April 2010, https://web.archive.org/web/20100404150912/http://www.kkbs.gov.bn/html/pakaian_tradisi.htm, retrieved on 20 July 2010
- Leyden, John (1821), Malay Annals: Translated from the Malay Language, London: Longman, Hurst, Rees, Orme, and Brown
- Littrup, Lisbeth (1996), Identity in Asian literature, Richmond: Nordic Institute of Asian Studies, ISBN 0-7007-0367-5
- Lockard, Craig A. (2009), Southeast Asia in world history, New York: Oxford University Press, ISBN 978-0-19-533811-9
- Lumholtz, Carl Sofus (2004), Through Central Borneo, Kessinger publishing, ISBN 978-1-4191-8996-8
- M. G. Husain (2007), Muslim identity and Islam: misinterpreted in the contemporary world, New Delhi: Manak Publications, ISBN 81-7827-165-6
- Majlis Kebudayaan Negeri Kedah (1986), Intisari kebudayaan Melayu Kedah: Kumpulan rencana mengenai kebudayaan Negeri Kedah, Majlis Kebudayaan Negeri Kedah
- Malaysia.com (2011), Nasi Lemak, http://www.malaysia.com/nasi-lemak-food.html, retrieved on 6 July 2010
- Marshall Cavendish (2007), World and Its Peoples: Eastern and Southern Asia, New York: Marshall Cavendish, ISBN 978-0-7614-7631-3
- Marzuki bin Haji Mohd Seruddin (2009), Program Kerjasama Brunei-Malaysia tingkatkan seni Budaya, Pelita Brunei, http://www.pelitabrunei.gov.bn/news/pelita/01julai/berita14.htm, retrieved on 15 June 2012
- Matusky, Patricia Ann (1993), Malaysian shadow play and music: continuity of an oral tradition, Oxford University Press, ISBN 967-65-3048-4
- Maznah Mohammad (1996), The Malay handloom weavers: a study of the rise and decline of traditional manufacture, Singapore: Institute of Southeast Asian Studies, ISBN 981-3016-99-X
- McNair, Sylvia (2002), Malaysia (Enchantment of the World. Second Series), Children's Press, ISBN 0-516-21009-2
- Melayu Online (2005), Melayu Online.com's Theoretical Framework, http://melayuonline.com/eng/about/dig/2
- Milner, Anthony (2010), The Malays (The Peoples of South-East Asia and the Pacific), Wiley-Blackwell, ISBN 978-1-4443-3903-1
- Ministry of Culture, Singapore (1973), Singapore: facts and pictures, ISSN 0217-7773
- Mohamad Tajuddin Haji Mohamad Rasdi (2005), The architectural heritage of the Malay world: the traditional houses, Kuala Lumpur: Penerbit UTM, ISBN 983-52-0357-1
- Mohamed Anwar Omar Din (2011), Asal Usul Orang Melayu: Menulis Semula Sejarahnya (The Malay Origin: Rewrite Its History), Jurnal Melayu, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, https://www.scribd.com/doc/82001895, retrieved on 4 June 2012
- Mohd. Aris Hj. Othman (1983), The dynamics of Malay identity, Penerbit Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, ISBN 978-967-942-009-8
- Mohd Fauzi Yaacob (2009), Malaysia: Transformasi dan perubahan sosial, Kuala Lumpur: Arah Pendidikan Sdn Bhd, ISBN 978-967-323-132-4
- Mohd. Zamberi A. Malek. (1994), Patani dalam tamadun Melayu, Pendeta Discovery Universiti Malaya, ISBN 9789836241214
- Moore, Wendy (1998), West Malaysia and Singapore, Singapore: Periplus Editions (HK) Ltd, ISBN 962-593-179-1
- Mysarawak.org (2009), Seni Bermukun Semakin Malap, http://www.mysarawak.org/2009/04/20/seni-bermukun-semakin-malap.html, retrieved on 15 June 2012
- Mukerjee, Radhakamal (1984), The culture and art of India, Coronet Books Inc, ISBN 978-81-215-0114-9
- Muljana, Slamet (1981), Kuntala, Sriwijaya Dan Suwarnabhumi, Yayasan Idayu
- Muljana, Slamet (2006), Stapel, Frederik Willem, ed., Sriwijaya, PT. LKiS Pelangi Aksara, ISBN 978-979-8451-62-1
- Munoz, Paul Michel (2006), Early Kingdoms of the Indonesian Archipelago and the Malay Peninsula, Singapore: Editions Didier Millet, ISBN 981-4155-67-5
- Murdock, George Peter (1969), Studies in the science of society, Singapore: Books for Libraries Press, ISBN 978-0-8369-1157-2
- Nik Anuar Nik Mahmud (1999), Sejarah Perjuangan Melayu Pattani, Bangi: Penerbit Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, ISBN 9789679424430
- O'Reilly, Dougald J. W. (2007), Early civilizations of Southeast Asia, Rowman Altamira Press, ISBN 978-0-7591-0278-1
- Omniglot (2012), Malay (Bahasa Melayu), http://www.omniglot.com/writing/malay.htm
- Ooi, Keat Gin (2004), Southeast Asia: a historical encyclopedia, from Angkor Wat to East Timor, ABC-CLIO, ISBN 1-57607-770-5
- Pande, Govind Chandra (2005), India's Interaction with Southeast Asia: History of Science, Philosophy and Culture in Indian Civilization, Vol. 1, Part 3, Munshiram Manoharlal, ISBN 978-81-87586-24-1
- Perpustakaan Negara Malaysia (2003), Royal and Palace Cutoms:Dresses For Ceremonies And Functions, http://www.malaysianmonarchy.org.my/malaysianmonarchy/?q=en/dress, retrieved on 20 July 2010
- Pogadaev, V.A. (2012), Malay World (Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore). Lingua-Cultural Dictionary), Vostochnaya Kniga, ISBN 978-5-7873-0658-3, http://www.pereplet.ru/news/index.cgi?id=30786#30786
- Rashahar Ramli (1999), Masyarakat Melayu dan penanaman padi di Selatan Thailand : kajian kes di sebuah mubaan dalam Wilayah / Narathiwat, UM Digital Repository, http://digitaleprints.um.edu.my/493/3/BAB2.pdf
- Richmond, Simon (2007), Malaysia, Singapore & Brunei, Lonely Planet publications, ISBN 978-1-74059-708-1
- Ryan, Neil Joseph (1976), A History of Malaysia and Singapore, London: Oxford University Press, ISBN 0-19-580302-7
- Sabrizain (2006), Early Malay kingdoms, http://www.sabrizain.org/malaya/early.htm
- Sarkar, Himansu Bhusan (1970), Some contributions of India to the ancient civilisation of Indonesia and Malaysia, Calcutta: Punthi Pustak, ISBN 0-19-580302-7
- Sheikh Shamsuddin (2005), The Malay art of self-defense: Silat Seni Gayung, Berkeley: North Atlantic Books, ISBN 1-55643-562-2
- Sneddon, James N. (2003), The Indonesian language: its history and role in modern society, University of New South Wales Press, ISBN 0-86840-598-1
- Srinivasa, Kodaganallur Ramaswami (2003), Asian variations in Ramayana, Singapore: Sahitya Academy, ISBN 81-260-1809-7
- Stearns, Peter N. (2001), The Encyclopedia of World History ( volume 1), Houghton Mifflin Harcourt, ISBN 978-0-395-65237-4
- Suryadinata, Leo (2000), Nationalism & Globalization: East & West, Institute of Southeast Asian Studies, ISBN 978-981-230-078-2
- Sweeney, Amin (1987), A full hearing:orality and literacy in the Malay world, Berkeley: University of California Press, ISBN 0-520-05910-7
- Syed Husin Ali (2008), The Malays, their problems and future, Kuala Lumpur: The Other Press Sdn Bhd, ISBN 978-983-9541-62-5
- Tan, Liok Ee (1988), The Rhetoric of Bangsa and Minzu, Monash Asia Institute, ISBN 978-0-86746-909-7
- TED (1999), Taman Negara Rain Forest Park and Tourism, http://www1.american.edu/ted/malayprk.htm
- The Art of Living Show (2011), For Sale - CountryHeights, YouTube, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7ZCHUMYs2CM&feature=plcp
- The Star (2008), Kedah MB defends use of Jawi on signboards, Archived from the original on 29 October 2012, https://web.archive.org/web/20121029105406/http://thestar.com.my/news/story.asp?file=%2F2008%2F8%2F26%2Fnation%2F22168989&sec=nation
- Tirtosudarmo, Riwanto (2005), The Orang Melayu and Orang Jawa in the 'Lands Below the Winds, Centre for research on inequality, human security and ethnicity, http://www.sabrizain.org/malaya/library/documents/146A9E1B75DB8163AE2228D170EC7D871787832B.html
- Tongkat Ali (2010), Negeri Rahman, hilangnya sebutir permata, http://kebunketereh.com/?p=387
- Umaiyah Haji Omar (2007), Language and writing system of Bangkok Melayu, http://www.sabrizain.org/malaya/library/bkmlang.pdf, retrieved on 15 June 2012
- Umaiyah Haji Omar (2003), The Assimilation of the Bangkok-Melayu Communities, Asian Scholarship Foundation, http://www.asianscholarship.org/asf/ejourn/articles/umaiyah_haji_umar.doc, retrieved on 15 June 2012
- Van Beek, Steve; Invernizzi, Luca (1999), The arts of Thailand, New York: Tuttle Publishing, ISBN 962-593-262-3
- Van der Putten, Jan; Cody, Mary Kilcline (2009), Lost Times and Untold Tales from the Malay World, Singapore: National University of Singapore press, ISBN 978-9971-69-454-8
- Winarno, Bondan (2011), Gulai Ketam, Asam-Asam Pedas, Detik Food, http://us.detikfood.com/read/2010/06/21/160229/1382992/908/gulai-ketam-asam-asam-pedas, retrieved on 15 January 2011
- Winstedt, Richard Olaf (1925), Shaman Saiva and Sufi (2008 edition), London: BiblioLife, ISBN 978-1-4346-8633-6
- Wolters, Oliver William (1999), History, culture, and region in Southeast Asian perspectives, Singapore: Cornell University Southeast Asia Program Publications, ISBN 978-0-87727-725-5
- Wong, Hoy Kee (1973), Comparative studies in Southeast Asian education, Heinemann Educational Books (Asia), ISBN 978-0-686-60339-9
- World Population Review (2015), Thailand, http://worldpopulationreview.com/countries/thailand-population/
- Wright, John (2007), The New York Times Almanac 2001, New York: The New York Times Company, ISBN 1-57958-348-2
- Wright, Thomas (2004), The travels of Marco Polo, the Venetian: the translation of Marsden revised, with a selection of his notes, Kessinger Publishing, LLC, ISBN 978-1-4191-8573-1
- Zaki Ragman (2003), Gateway to Malay culture, Singapore: Asiapac Books Pte Ltd, ISBN 981-229-326-4
- Ziegler, Oswald Leopol (1972), The world and south east Asia, Oswald Ziegler Enterprises, ISBN 0-909586-03-9
الكلمات الدالة:
This article contains content from Wikimedia licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0. Please comply with the license terms.
تصنيفات:
- Articles with hatnote templates targeting a nonexistent page
- Pages using infobox ethnic group with unsupported parameters
- Articles using infobox ethnic group with image parameters
- Articles containing ملايو (لغة كبرى)-language text
- Pages using Lang-xx templates
- قوائم غير مكتملة
- Pages using div col with unknown parameters
- ملايويون
- جماعات عرقية في جنوب شرق آسيا
- جماعات لسانية عرقية في آسيا
- ملايو
- شبه جزيرة الملايو
- جماعات عرقية في بروناي
- جماعات عرقية في سومطرة
- جماعات عرقية في ماليزيا
- جماعات عرقية في ساراواك
- جنوب شرق آسيا البحري



