ڤـِنـِتو
ڤـِنـِتو | |
|---|---|
 | |
| البلد | إيطاليا |
| العاصمة | Venice |
| الحكومة | |
| • الرئيس | Luca Zaia (Liga Veneta–Lega Nord) |
| المساحة | |
| • الإجمالي | 18٬399 كم² (7٬104 ميل²) |
| التعداد (2012-10-30) | |
| • الإجمالي | 4٬865٬380 |
| • الكثافة | 260/km2 (680/sq mi) |
| الجنسية | |
| • الإيطالية | 92% |
| • Romanian | 2% |
| • Moroccan | 1% |
| منطقة التوقيت | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • الصيف (التوقيت الصيفي) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| ن.م.إ./ الإسمي | 149.4[2] بليون € (2008) |
| ن.م.إ. للفرد | €30,500[3] (2008) |
| منطقة NUTS | ITD |
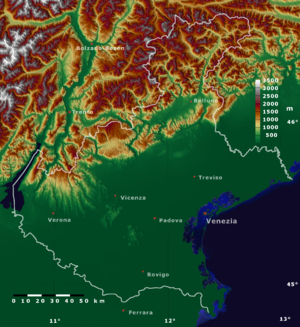
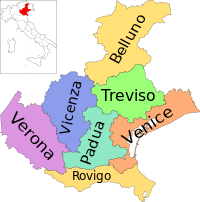
فينيتو (بالإيطالية: Veneto ) ، أحد أقاليم إيطاليا العشرين ، يقع في شمال شرق إيطاليا ، عدد سكانها 4.759.872 نسمة و مساحته 18391,22 كيلومتر مربع ، و عدد مدنه و بلداته و قراه 581 ، عاصمة الاقليم هي البندقية. يعتبر الإقليم من أغنى الأقاليم الإيطالية من ناحية المعالم والاماكن التاريخية و خصوصا اثار عصر النهضة التي تمثل ذروتها في البندقية و كذلك أماكن تاريخية ترجع إلى الحضارة الرومانية. اقتصادها الذي كان يتكل في السابق على الزراعة و الضرائب بات الآن اقتصاد صناعي مزدهر ومقر لبعض دور الأزياء الايطالية و كذلك قطاع السياحة الذي يساهم في اقتصاد الأقليم خاصة و إيطاليا عامة نظرا لما يتمتع به الاقليم من مزايا . تتكون من سبعة مقاطعات وهي :



أهم المدن
| المدينة | الإسم بالإيطالية | المقاطعة | السكان |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. فينيسيا | Venezia | فينيسيا | 271.251 |
| 2. فيرونا | Verona | فيرونا | 259.068 |
| 3. بادوفا | Padova | بادوفا | 210.938 |
| 4. فيشنزا | Vicenza | فيشنزا | 113.483 |
| 5. تريفيزو | Treviso | تريفيزو | 82.399 |
| 6. كيودجا | Chioggia | فينيسيا | 51.336 |
| 7. روفيغو | Rovigo | روفيغو | 50.883 |
| 8. باسانو دل غرابا | Bassano del Grappa | فيشنزا | 40.411 |
| 9. سان دونا دي بيافي | San Donà di Piave | فينيسيا | 38.904 |
| 10. سكيو | Schio | فيشنزا | 38.638 |
| 11. ميرا | Mira | فينيسيا | 37.737 |
| 12. بيلونو | Belluno | بيلونو | 35.598 |
| 13. كونيليانو | Conegliano | تريفيزو | 35.520 |
| 14. كاستيلفرانكو فينيتو | Castelfranco Veneto | تريفيزو | 32.975 |
| 15. فيلافرانكا دي فيرونا | Villafranca di Verona | فيرونا | 30.521 |
القطاعات الاقتصادية
The main sectors in the economy of Veneto are:
| Economic activity | GDP product | % sector (region) | % sector (Italy) |
| Primary (agriculture, farming, fishing) | € 2,303.3 | 1.66% | 1.84% |
| Secondary (industry, processing, manufacturing) | € 34,673.6 | 24.95% | 18.30% |
| Constructions | € 8,607.7 | 6.19% | 5.41% |
| Tertiary (Commerce, hotels and restaurants, tourism, (tele)communications and transport) | € 28,865.8 | 20.77% | 20.54% |
| Financial activities and real estate | € 31,499.4 | 22.66% | 24.17% |
| Other types of services | € 19,517.2 | 14.04% | 18.97% |
| VAT and taxes | € 13,526.4 | 9.73% | 10.76% |
| GDP of Veneto | € 138,993.5 |
UNESCO World Heritage Sites
| Name and description | Image |
|---|---|
|
Inserted by UNESCO in 1997. It is the world's oldest academic botanical garden that is still in its original location. (Officially, the oldest university botanical garden is the Orto botanico di Pisa, which was founded in 1544; however, that garden was relocated twice and has only occupied its current, and now-permanent, location since 1591.) It is located in Padua, Italy and was founded in 1545. The garden, affiliated with the University of Padua, currently covers roughly 22,000 square meters and has special collections. |
|
|
Verona was inscribed in the year 2000. One of the seven provincial capitals in the region. It is one of the main tourist destinations in north-eastern Italy, thanks to its artistic heritage, several annual fairs, shows and operas, such as the lyrical season in the Arena, the ancient amphitheatre built by the Romans. |
|
|
The city and the Palladian Villas of Veneto were inscribed in 1994. Vicenza is a thriving and cosmopolitan city, with a rich history and culture, and many museums, art galleries, piazzas, villas, churches and elegant, Renaissance palazzi. The Palladian Villas of Veneto, in the surrounding area, and the renowned Teatro Olimpico (Olympic Theatre) have both been enlisted as UNESCO World Heritage Sites since 1994.[5] |
|
|
The city and its lagoon were inscribed in 1987. With a population of 271,367 (census estimate 1 January 2004). Together with Padua, the city is included in the Padua-Venice Metropolitan Area (population 1,600,000). The city historically was the capital of an independent nation. Venice has been known as the "La Dominante", "Serenissima", "Queen of the Adriatic", "City of Water", "City of Bridges", "City of Canals" and "The City of Light". Luigi Barzini, writing in The New York Times, described it as "undoubtedly the most beautiful city built by man".[6] Venice has also been described by the Times Online as being one of Europe's most romantic cities.[7] |
|
|
They were inscribed in 2009. They are located for the most part in the province of Belluno, the rest in South Tyrol and Trentino (all in north-eastern Italy). Conventionally they extend from the Adige river in the west to the Piave valley (Pieve di Cadore) in the east. The northern and southern borders are defined by the Puster Valley and the Sugana Valley (Val Sugana). But the Dolomites spread also over the Piave river (Dolomiti d'Oltrepiave) to the east; and far away over the Adige river to the west is the Brenta Group (Western Dolomites); there is also another smaller group called Piccole Dolomiti (Small Dolomites) located between the Provinces of Trento and Vicenza (see the map). |
Palladian Villas of Veneto
الهامش
- ^ "Statistiche demografiche ISTAT". Demo.istat.it. Retrieved 2010-04-24.
- ^ "Eurostat - Tables, Graphs and Maps Interface (TGM) table". Epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu. 2011-03-11. Retrieved 2011-06-03.
- ^ "Regional GDP per inhabitant in 2008 GDP per inhabitant ranged from 28% of the EU27 average in Severozapaden in Bulgaria to 343% in Inner London". Europa.eu. 2011-02-24. Retrieved 2012-05-06.
- ^ "World Heritage Centre - World Heritage List". Whc.unesco.org. Retrieved 2010-01-25.
- ^ Moretti, John (2008-06-16). Frommer's Northern Italy: Including ... - Google Books. Books.google.co.uk. ISBN 978-0-470-18193-5. Retrieved 2010-01-25.
- ^ Barzini, Luigi (1982-05-30). "The Most Beautiful City In The World - The". New York Times. Retrieved 2009-03-28.
- ^ Europe's most romantic city breaks[dead link]
وصلات خارجية
- Articles with dead external links from April 2010
- Short description is different from Wikidata
- Articles with unsourced statements from October 2011
- Pages using infobox settlement with unknown parameters
- Pages using infobox settlement with no coordinates
- Veneto
- Regions of Italy
- أقاليم التصنيف الثاني في الاتحاد الأوروپي
- Wine regions of Italy
- أقاليم إيطاليا