سبيرونولاكتون
 | |
| البيانات السريرية | |
|---|---|
| أسماء أخرى | Aldactone Spirotone Spirolactone |
| فئة السلامة أثناء الحمل |
|
| مسارات الدواء | Oral |
| رمز ATC | |
| الحالة القانونية | |
| الحالة القانونية | |
| بيانات الحركية الدوائية | |
| الأيض | Hepatic |
| Elimination half-life | 10 minutes |
| الإخراج | Urine, bile |
| المعرفات | |
| |
| رقم CAS | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.122 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| التركيب | C24H32O4S |
| الكتلة المولية | 416.574 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| (verify) | |
السبيرونولاكتون إنگليزية: Spironolactone من المدرات الحافظة للبوتاسيوم، يُستعمل في علاج ارتفاع ضغط الدم بالمشاركه مع المدرات التيازيديه، كما يستخدم في علاج قصور القلب بتركيز أقل، ويجب عند وصفه مراقبة مستوى البوتاسيوم في الدم بشكل دوري لأن السبيرونولاكتون يؤدي في بعض الأحيان إلى رفع مستوى البوتاسيوم في الدم لمستويات خطيرة
قد تؤدي إلى لانظميات خطرة.
نظراً لبنيته الكيميائية الشبيهة بمادة التستوستيرون فإن السبيرانولاكتون يمكنه أن يمنع تأثيره.. بأن يستقر في مستقبلات التستوستيرون و يعمل حجب لتأثيرها ..و من هذا المنطلق يقوم بعض الأطباء بوصفه لعلاج تساقط الشعر الأندروجيني و خاصة عند النساء ..
و كما يقلل من شعرانية الجسم (ما عدا شعر الرأس) أو ما يسمى hirsutism لنفس الخاصية المذكورة بالأعلى ..
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
آلية التأثير
يعمل السبيرونولاكتون على تثبيط فعل الألدسترون عن طريق التنافس على مستقبلاته داخل الخلوية في القناة الجامعة القشرية. يؤدي هذا إلى إنقاص إعادة امتصاص الصوديوم و الماء و إنقاص إفراز البوتاسيوم. تكون بداية تأثير السبيرونولاكتون بطيئة نوعا ما, بحيث يستغرق عدة أيام لتظهر ولذلك فإن الأثر العلاجي يكون بطيء. وهذا بسبب تعديل مسار نسخ الجينات الستيروئيدية, ويتطلب عدة أيام لمنتجات الجين لتقوم بالتغيير (في هذه الحالة سيتم تثبيط قنوات إيناك و رومك). يمتلك السبيرونولاكتون فعالية مضادة للأندروجين كونه يرتبط إلى المستقبلات الأندروجينية مانعاً إياه من التفاعل مع الدي هيدروتستسترون.
Spironolactone inhibits the effect of aldosterone by competing for intracellular aldosterone receptors in the cortical collecting duct. This decreases the reabsorption of sodium and water, while decreasing the secretion of potassium. Spironolactone has a fairly slow onset of action, taking several days to develop, and, so, the effect diminishes slowly. This is because steroid pathways alter gene transcription, and it will take several days for the gene products to change (in this case the ENaC and ROMK channels will be decreased). Spironolactone has anti-androgen activity by binding to the androgen receptor and preventing it from interacting with dihydrotestosterone.[1]
الحركية الدوائية
Spironolactone is a synthetic steroid that acts as a competitive antagonist to aldosterone. Its onset and duration of action are determined by the kinetics of the aldosterone response in the target tissue. Substantial inactivation of spironolactone occurs in the liver and hepatitis or cirrhosis can lead to secondary aldosteronism, which is one indication for treatment. Overall, spironolactone has a rather slow onset of action, requiring several days before full therapeutic effect is achieved.
Mortality and morbidity benefit in severe heart failure
Spironolactone was shown to have a significant mortality and morbidity benefit in the Randomized Aldactone Evaluation Study (RALES), which studied people with severe congestive heart failure (New York Heart Association functional class III or IV).[2] Patients in the study arm of the trial (those receiving spironolactone) had a relative risk of death (when compared to the placebo group) equal to 0.70 or a 30% relative risk reduction. Patients in the study arm also had fewer symptoms of CHF and were hospitalized less frequently.
The mechanism of this effect is also mediated by inhibiting aldosterone, which in conjunction with heart failure leads to myocardial remodeling including fibrosis, sodium retention, and vascular dysfunction.
Adverse effects and interactions
Spironolactone is associated with an increased risk of bleeding from the stomach and duodenum, but a causal relationship between the two has not been established.[3] Because it also affects androgen receptors and other steroid receptors, it can cause gynecomastia, menstrual irregularities and testicular atrophy. Other side effects include ataxia, erectile dysfunction, drowsiness, and rashes. A carcinogenic effect has been demonstrated in rats, see below. Spironolactone has been shown to be immunosuppressive in the treatment of sarcoidosis.[4]
Spironolactone often increases serum potassium levels and can cause hyperkalemia, a very serious condition. Therefore, it is recommended that people using this drug avoid potassium supplements and salt substitutes containing potassium.[5] Doctors usually recommend periodic screening of serum potassium levels and some patients may be advised to limit dietary consumption of potassium.
Research has also shown spironolactone can interfere with the effectiveness of antidepressant treatment. The drug is actually (among its other receptor interactions) a mineralocorticoid (MR) antagonist, and has been found to reduce the effectiveness of antidepressant drugs in the treatment of major depression, it is presumed, by interfering with normalization of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in patients receiving antidepressant therapy.[6]
Carcinogenicity
Studies of spironolactone and the related compound potassium canrenoate (which, like spironolactone, metabolizes to canrenone) in rats for one- to two-year periods show an increase in carcinogenesis in the thyroid gland, testes, liver, breasts, and myelocytic leukocytes. Mammalian cells, depending on the presence of metabolic activation, show mixed results for mutagenicity in vitro.[7] Doses relative to body weight were 10 to 150 mg per kg, which is ten to 500 times higher than normal doses for treating humans. In light of this research, Sandoz has recommended that unnecessary use of spironolactone be avoided.
Other potential benefits
It has been suggested that spironolactone can reduce the risk of Alzheimer's disease. In one study,[8] researchers observed a reduction in the risk of Alzheimer's specifically associated with potassium-sparing diuretics. Unpublished findings from other studies, including the Gothenberg Study have suggested that higher potassium levels may be associated with a lower risk of dementia.
Spironolactone may have antifibrotic properties[بحاجة لمصدر] and an NIH-sponsored randomized control trial of treatment of patients with diastolic heart failure with this drug, known as the TOPCAT Study has been planned (heart failure patients with diastolic dysfunction have evidence of active collagen metabolism and increasing fibrosis[بحاجة لمصدر]).
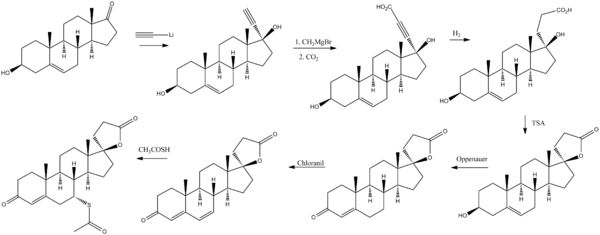
الاصطناع
Cella, John A.; Tweit, Robert C. (1959). Journal of Organic Chemistry. 24: 1109. doi:10.1021/jo01090a019. {{cite journal}}: Missing or empty |title= (help)
(See also part 1 and part 3)
Spironolactone bodies
Long-term administration of spironolactone gives the histologic characteristic of spironolactone bodies in the adrenal cortex. Spironolactone bodies are eosinophilic, round, concentrically laminated cytoplasmic inclusions surrounded by clear halos in preparations stained with hematoxylin and eosin.[9]
انظر أيضا
المصادر
- ^ Berardesca, E (1988). "Topical spironolactone inhibits dihydrotestosterone receptors in human sebaceous glands: an autoradiographic study in subjects with acne vulgaris". Int J Tissue React. 10 (2): 115–119. PMID 2972662.
{{cite journal}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Pitt B, Zannad F, Remme W, Cody R, Castaigne A, Perez A, Palensky J, Wittes J (1999). "The effect of spironolactone on morbidity and mortality in patients with severe heart failure. Randomized Aldactone Evaluation Study Investigators". N Engl J Med. 341 (10): 709–17. doi:10.1056/NEJM199909023411001. PMID 10471456.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Verhamme KMC, Mosis G, Dieleman JP; et al. (2006). "Spironolactone and risk of upper gastrointestinal events: population based case-control study". Brit Med J. 333 (7563): 330–3. doi:10.1136/bmj.38883.479549.2F. PMC 1539051. PMID 16840442.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Wandelt-Freerksen E. (1977). "Aldactone in the treatment of sarcoidosis of the lungs". JZ Erkr Atmungsorgane. 149 (1): 156–9. PMID 607621.
{{cite journal}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - ^ "Advisory Statement" (PDF). Klinge Chemicals / LoSalt. Archived from the original (pdf) on 2006-11-15. Retrieved 2007-03-15.
- ^ Holsboer, F. The Rationale for Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone Receptor (CRH-R) Antagonists to Treat Depression and Anxiety. J. Psychiatr. Res. 33, 181–214 (1999)
- ^ "Spironolactone RX Monograph". Sandoz Inc. Retrieved 2007-05-02.
- ^ [archneur.ama-assn.org/cgi/content/full/63/5/686 Antihypertensive Medication Use and Incident Alzheimer Disease]. Arch Neurol. 2006;63:686-692. Published online March 13, 2006 (doi:10.1001/archneur.63.5.noc60013)
- ^ Aiba M, Suzuki H, Kageyama K; et al. (1981). "Spironolactone bodies in aldosteronomas and in the attached adrenals. Enzyme histochemical study of 19 cases of primary aldosteronism and a case of aldosteronism due to bilateral diffuse hyperplasia of the zona glomerulosa". Am. J. Pathol. 103 (3): 404–10. PMC 1903848. PMID 7195152.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
روابط خارجية
- CS1 errors: unsupported parameter
- CS1 errors: access-date without URL
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Infobox-drug molecular-weight unexpected-character
- Pages using infobox drug with unknown parameters
- Articles without EBI source
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without InChI source
- Articles containing إنگليزية-language text
- Articles with unsourced statements from January 2010
- CS1 errors: missing title
- Aldosterone antagonists
- Antiandrogens
- مدرات البول
- الأدوية الأساسية حسب منظمة الصحة العالمية
- Furones
- Spiro compounds