محرك حراري
| ثرموديناميكا |
|---|
 |
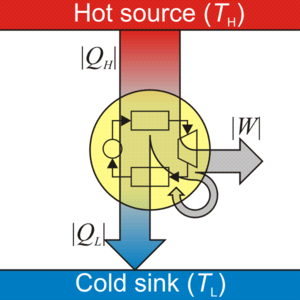
المحرك الحراري هو جهاز نظري أو عملي يقوم بتحويل الطاقة الحرارية إلى خرج ميكانيكي. يسمى الخرج الميكانيكي بالعمل، والطاقة الحرارية المُدخلة بالحرارة. تعمل المحركات الميكانيكية في دورات حرارية خاصة، كما يمكن أن تكون هذه المحركات مفتوحة على الهواء، أو مغلقة. (دورة مفتوحة أو مغلقة). في الهندسة والديناميكية الحرارية يقوم المحرك الحراري بتحويل الطاقة الحرارية إلى عمل ميكانيكي عن طريق استغلال التدرج في الحرارة بين مصدر ساخن و حوض حرارة بارد.
تنتقل الحرارة من المصدر، مروراً بالجسم العامل من المحرك، إلى الحوض، وأثناء هذه العملية يتحول جزء من الحرارة إلى عمل عن طريق استغلال خصائص المادة العاملة (عادة ما تكون غازية أو سائلة). The working substance generates work in the working body of the engine while transferring heat to the colder sink until it reaches a lower temperature state. During this process some of the thermal energy is converted into work by exploiting the properties of the working substance. The working substance can be any system with a non-zero heat capacity, but it usually is a gas or liquid. During this process, some heat is normally lost to the surroundings and is not converted to work. Also, some energy is unusable because of friction and drag.
In general, an engine is any machine that converts energy to mechanical work. Heat engines distinguish themselves from other types of engines by the fact that their efficiency is fundamentally limited by Carnot's theorem of thermodynamics.[1] Although this efficiency limitation can be a drawback, an advantage of heat engines is that most forms of energy can be easily converted to heat by processes like exothermic reactions (such as combustion), nuclear fission, absorption of light or energetic particles, friction, dissipation and resistance. Since the heat source that supplies thermal energy to the engine can thus be powered by virtually any kind of energy, heat engines cover a wide range of applications.
Heat engines are often confused with the cycles they attempt to implement. Typically, the term "engine" is used for a physical device and "cycle" for the models.
استعراض
In thermodynamics, heat engines are often modeled using a standard engineering model such as the Otto cycle. The theoretical model can be refined and augmented with actual data from an operating engine, using tools such as an indicator diagram. Since very few actual implementations of heat engines exactly match their underlying thermodynamic cycles, one could say that a thermodynamic cycle is an ideal case of a mechanical engine. In any case, fully understanding an engine and its efficiency requires a good understanding of the (possibly simplified or idealised) theoretical model, the practical nuances of an actual mechanical engine and the discrepancies between the two.
In general terms, the larger the difference in temperature between the hot source and the cold sink, the larger is the potential thermal efficiency of the cycle. On Earth, the cold side of any heat engine is limited to being close to the ambient temperature of the environment, or not much lower than 300 kelvin, so most efforts to improve the thermodynamic efficiencies of various heat engines focus on increasing the temperature of the source, within material limits. The maximum theoretical efficiency of a heat engine (which no engine ever attains) is equal to the temperature difference between the hot and cold ends divided by the temperature at the hot end, each expressed in absolute temperature.
The efficiency of various heat engines proposed or used today has a large range:
- 3%[2] (97 percent waste heat using low quality heat) for the ocean thermal energy conversion (OTEC) ocean power proposal
- 25% for most automotive gasoline engines[3]
- 49% for a supercritical coal-fired power station such as the Avedøre Power Station
- 60% for a combined cycle gas turbine[4]
The efficiency of these processes is roughly proportional to the temperature drop across them. Significant energy may be consumed by auxiliary equipment, such as pumps, which effectively reduces efficiency.
أمثلة
Although some cycles have a typical combustion location (internal or external), they can often be implemented with the other. For example, John Ericsson[5] developed an external heated engine running on a cycle very much like the earlier Diesel cycle. In addition, externally heated engines can often be implemented in open or closed cycles. In a closed cycle the working fluid is retained within the engine at the completion of the cycle whereas is an open cycle the working fluid is either exchanged with the environment together with the products of combustion in the case of the internal combustion engine or simply vented to the environment in the case of external combustion engines like steam engines and turbines. فعلى سبيل المثال، طور جون إريكسون محرك يـُسخـَّن خارجياً يعمل على دورة شديدة الشبه لدورة الديزل السابقة له.
Everyday examples
Everyday examples of heat engines include the thermal power station, internal combustion engine, firearms, refrigerators and heat pumps. Power stations are examples of heat engines run in a forward direction in which heat flows from a hot reservoir and flows into a cool reservoir to produce work as the desired product. Refrigerators, air conditioners and heat pumps are examples of heat engines that are run in reverse, i.e. they use work to take heat energy at a low temperature and raise its temperature in a more efficient way than the simple conversion of work into heat (either through friction or electrical resistance). Refrigerators remove heat from within a thermally sealed chamber at low temperature and vent waste heat at a higher temperature to the environment and heat pumps take heat from the low temperature environment and 'vent' it into a thermally sealed chamber (a house) at higher temperature.
In general heat engines exploit the thermal properties associated with the expansion and compression of gases according to the gas laws or the properties associated with phase changes between gas and liquid states.
Earth's heat engine
Earth's atmosphere and hydrosphere—Earth's heat engine—are coupled processes that constantly even out solar heating imbalances through evaporation of surface water, convection, rainfall, winds and ocean circulation, when distributing heat around the globe.[6]
A Hadley cell is an example of a heat engine. It involves the rising of warm and moist air in the earth's equatorial region and the descent of colder air in the subtropics creating a thermally driven direct circulation, with consequent net production of kinetic energy.[7]
دورات تغير الأطوار
In these cycles and engines, the working fluids are gases and liquids. The engine converts the working fluid from a gas to a liquid.
- دورة رانكين (classical steam engine)
- Regenerative cycle (steam engine more efficient than Rankine cycle)
- Vapor to liquid cycle (Drinking bird, Injector, Minto wheel)
- Liquid to solid cycle (Frost heaving — water changing from ice to liquid and back again can lift rock up to 60 m.)
- Solid to gas cycle (Dry ice cannon — Dry ice sublimes to gas.)
دورات غازية فقط
In these cycles and engines the working fluid is always a gas (ie, there is no phase change):
- دورة كارنو (محرك كارنو الحراري)
- دورة إريكسون (Caloric Ship John Ericsson)
- Stirling cycle (Stirling engine, thermoacoustic devices)
- محرك الاحتراق الداخلي (ICE):
- Otto cycle (eg. Gasoline/Petrol engine, high-speed diesel engine)
- دورة الديزل (eg. low-speed diesel engine)
- Atkinson Cycle (محرك أتكنسون)
- Brayton cycle or Joule cycle originally Ericsson Cycle (توربين غازي)
- Lenoir cycle (e.g., pulse jet engine)
- دورة ميلر
دورات سائلة فقط
In these cycles and engines the working fluid are always like liquid:
دورات الإلكترون
- Thermoelectric (Peltier-Seebeck effect)
- Thermionic emission
- Thermotunnel cooling
دورات مغناطيسية
- Thermo-magnetic motor (تسلا)
الدورات المستعملة للتبريد
A refrigerator is a heat pump: a heat engine in reverse. Work is used to create a heat differential. Many cycles can run in reverse to move heat from the cold side to the hot side, making the cold side cooler and the hot side hotter. Internal combustion engine versions of these cycles are, by their nature, not reversible.
- Vapor-compression refrigeration
- Stirling engine#Stirling cryocoolers
- Gas-absorption refrigerator
- Air cycle machine
- Vuilleumier refrigeration
المحركات الحرارية التبخرية
The Barton Evaporation Engine is a heat engine based on a cycle producing power and cooled moist air from the evaporation of water into hot dry air.
الكفاءة
The efficiency of a heat engine relates how much useful power is output for a given amount of heat energy input.
من قوانين الثرموديناميكا:
- حيث
- is the work extracted from the engine. (It is negative since work is done by the engine.)
- is the heat energy taken from the high temperature system. (It is negative since heat is extracted from the source, hence is positive.)
- is the heat energy delivered to the cold temperature system. (It is positive since heat is added to the sink.)
كفاءة المحركات الحرارية endoreversible
A different measure of ideal heat engine efficiency is given by considerations of endoreversible thermodynamics, where the cycle is identical to the Carnot cycle except in that the two processes of heat transfer are not reversible (Callen 1985):
This model does a better job of predicting how well real-world heat engines can do (Callen 1985, see also endoreversible thermodynamics):
| Power Plant | (°C) | (°C) | (Carnot) | (Endoreversible) | (Observed) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| West Thurrock (المملكة المتحدة) coal-fired power plant | 25 | 565 | 0.64 | 0.40 | 0.36 |
| CANDU (كندا) مفاعل طاقة نووية | 25 | 300 | 0.48 | 0.28 | 0.30 |
| Larderello (إيطاليا) geothermal power plant | 80 | 250 | 0.33 | 0.178 | 0.16 |
As shown, the endoreversible efficiency much more closely models the observed data.
عمليات المحرك الحراري
| الدورة/العملية | انضغاط | اضافة حرارة | تمدد | رفض حراري |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| دورات طاقة عادة ما يصحبها احتراق خارجي | ||||
| كارنو | adiabatic | isothermal | adiabatic | isothermal |
| Stirling | isothermal | isometric | isothermal | isometric |
| Ericsson | isothermal | isobaric | isothermal | isobaric |
| رانكين (بخار) | adiabatic | isobaric | adiabatic | isobaric |
| Stoddard | adiabatic | isobaric | adiabatic | isobaric |
| دورات طاقة عادة ما يصحبها احتراق داخلي | ||||
| اوتو (پترول) | adiabatic | isometric | adiabatic | isometric |
| ديزل | adiabatic | isobaric | adiabatic | isometric |
| برايتون (نفاث) | adiabatic | isobaric | adiabatic | isobaric |
كل عملية هي واحدة من التالين:
- isothermal (عند درجة حرارة ثابتة، محفوظة باضافة أو ازالة حرارة من مصدر أو بالوعة حرارية)
- isobaric (at constant pressure)
- isometric/isochoric (at constant volume), also referred to as iso-volumetric
- adiabatic (no heat is added or removed from the system during adiabatic process which is equivalent to saying that the entropy remains constant)
المصادر
- ^ Thermal physics: entropy and free energies, by Joon Chang Lee (2002), Appendix A, p. 183: "A heat engine absorbs energy from a heat source and then converts it into work for us.... When the engine absorbs heat energy, the absorbed heat energy comes with entropy." (heat energy ), "When the engine performs work, on the other hand, no entropy leaves the engine. This is problematic. We would like the engine to repeat the process again and again to provide us with a steady work source. ... to do so, the working substance inside the engine must return to its initial thermodynamic condition after a cycle, which requires to remove the remaining entropy. The engine can do this only in one way. It must let part of the absorbed heat energy leave without converting it into work. Therefore the engine cannot convert all of the input energy into work!"
- ^ Eman, Mahmod Mohamed (June 2013). "Experimental Investigations on a Standing-Wave Thermoacoustic Engine". ResearchGate. Giza, Egypt: Cairo University. Retrieved 21 January 2018.
- ^ Where the Energy Goes: Gasoline Vehicles, US Dept of Energy
- ^ Langston, Lee S. "Efficiency by the Numbers". ASME. Archived from the original on 16 June 2009.
- ^ "Ericsson's 1833 caloric engine". hotairengines.org.
- ^ Lindsey, Rebecca (2009). "Climate and Earth's Energy Budget". NASA Earth Observatory.
- ^ Junling Huang and Michael B. McElroy (2014). "Contributions of the Hadley and Ferrel Circulations to the Energetics of the Atmosphere over the Past 32 Years". Journal of Climate. 27 (7): 2656–2666. Bibcode:2014JCli...27.2656H. doi:10.1175/jcli-d-13-00538.1. S2CID 131132431.
- Kittel, Charles ; Kroemer, Herbert (2000). Thermal Physics (2nd ed. ed.). W. H. Freeman Company. ISBN 0-7167-1088-9.
{{cite book}}:|edition=has extra text (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Callen, Herbert B. (1985). Thermodynamics and an Introduction to Thermostatistics (2nd ed. ed.). John Wiley & Sons, Inc. ISBN 0-471-86256-8.
{{cite book}}:|edition=has extra text (help)
انظر أيضاً
- Reciprocating engine for a general description of the mechanics of piston engines
- Adiabatic engine
- Heat pump
- محرك كارنو الحراري
- Timeline of heat engine technology
- Heat engine classifications
- Thermosynthesis
وصلات خارجية
- Video of Stirling engine running on dry ice
- Heat Engine
- On line museum of toy steam engines, including a very rare Bing heat engine
- Webarchive backup: Refrigeration Cycle Citat: "...The refrigeration cycle is basically the Rankine cycle run in reverse..."
- Red Rock Energy Solar Heliostats: Heat Engine Projects Citat: "...Choosing a Heat Engine..."
- Overview of heat engine types - not working
- The rotary piston array machine
- The gyroscope combustion motor
- The external combustion air engine
- Super-efficient Atkinson-Diesel Cycle
| مواضيع الفيزياء الكلاسكية والأمواج وديناميكا حرارية |
|---|

|