بياويستوك
بياويستوك
Białystok | |
|---|---|
 | |
| الإحداثيات: 53°08′07″N 23°08′44″E / 53.13528°N 23.14556°E | |
| البلد | |
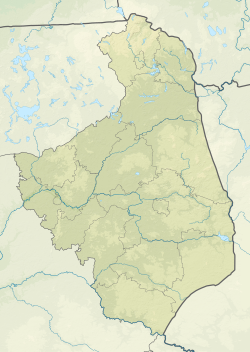
| Voivodeship | قالب:Country data Podlaskie Voivodeship |
| County | city county |
| Established | 1437 |
| Town rights | 1692 |
| Districts | |
| الحكومة | |
| • العمدة | Tadeusz Truskolaski[2] (PO) |
| المساحة | |
| • المدينة | 102٫12 كم² (39٫43 ميل²) |
| أعلى منسوب | 160 m (520 ft) |
| أوطى منسوب | 120 m (390 ft) |
| التعداد (31 December 2019) | |
| • الكثافة | 2٬910/km2 (7٬500/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 297٬554 ▲ (10th)[3] |
| • العمرانية | 430٬000 |
| منطقة التوقيت | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • الصيف (التوقيت الصيفي) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Postal code | 15-001 |
| مفتاح الهاتف | +48 85 |
| Car plates | BI |
| الموقع الإلكتروني | www |
 | |
Białystok (UK: /biːˈælɪstɒk/,[4] US: /biːˈɑːlɪstɔːk, ˈbjɑː-, bjɑːˈwɪstɔːk/,[5][6][7] پولندية: [bjaˈwɨstɔk] (![]() استمع); بالبيلاروسية: Беласток, تـُنطـَق [bʲɛlaˈstɔk]; لتوانية: Balstogė) is the largest city in northeastern Poland and the capital of the Podlaskie Voivodeship. Białystok is the tenth-largest city in Poland, second in terms of population density, and thirteenth in area.
استمع); بالبيلاروسية: Беласток, تـُنطـَق [bʲɛlaˈstɔk]; لتوانية: Balstogė) is the largest city in northeastern Poland and the capital of the Podlaskie Voivodeship. Białystok is the tenth-largest city in Poland, second in terms of population density, and thirteenth in area.
Białystok is located in the Białystok Uplands of the Podlaskie Plain on the banks of the Biała River. It has historically attracted migrants from elsewhere in Poland and beyond, particularly from Central and Eastern Europe. This is facilitated by the nearby border with Belarus also being the eastern border of the European Union, as well as the Schengen Area. The city and its adjacent municipalities constitute Metropolitan Białystok. The city has a warm summer continental climate, characterized by warm summers and long frosty winters. Forests are an important part of Białystok's character, and occupy around 1,756 ha (4,340 acres) (17.2% of the administrative area of the city) which places it as the fifth-most forested city in Poland.
The first settlers arrived in the 14th century. A town grew up and received its municipal charter in 1692. Białystok has traditionally been one of the leading centers of academic, cultural, and artistic life in Podlachia and the most important economic center in northeastern Poland. Białystok was once an important center for light industry, which was the reason for the substantial growth of the city's population. The city continues to reshape itself into a modern middle-sized city. Białystok, in 2010, was on the short-list, but ultimately lost the competition, to become a finalist for European Capital of Culture in 2016.
Etymology
The English translation of Białystok is "white slope".[8] Due to changing borders and demographics over the centuries, the city has been known as بالبيلاروسية: Беласток (Byelastok?, Biełastok? [bʲeɫaˈstok]), باليديشية: ביאַליסטאָק (Byalistok, Bjalistok), لتوانية: Baltstogė, Balstogė, and روسية: Белосток (Byelostok).
Linguist A. P. Nepokupnyj proposes that the language source for Białystok is Yotvingian. Names with the -stok suffix as a second element of a hydronym are localized in the basin of the upper Narew.[9]
التاريخ

Archaeological discoveries show that the first settlements in the area of present-day Białystok occurred during the Stone Age. Tombs of ancient settlers can be found in the district of Dojlidy.[10] In the early Iron Age, people settled in the area producing kurgans, the tombs of the chiefs in the area located in the current village of Rostołty.[11] Since then, the Białystok area has been at the crossroads of cultures. Trade routes linking the Baltic to the Black Sea favored the development of settlements with Yotvingia-Ruthenian-Polish cultural characteristics.[11]
الجغرافيا
المناخ
| بيانات المناخ لـ بياويستوك، المعتادة 1980–2012 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| الشهر | ينا | فب | مار | أبر | ماي | يون | يول | أغس | سبت | أكت | نوف | ديس | السنة |
| القصوى القياسية °س (°ف) | 12.0 (53.6) |
16.4 (61.5) |
20.0 (68.0) |
27.8 (82.0) |
31.1 (88.0) |
32.6 (90.7) |
36.1 (97.0) |
35.2 (95.4) |
31.1 (88.0) |
23.9 (75.0) |
17.2 (63.0) |
13.9 (57.0) |
36.1 (97.0) |
| متوسط القصوى اليومية °س (°ف) | −1.0 (30.2) |
−0.2 (31.6) |
4.9 (40.8) |
12.4 (54.3) |
18.4 (65.1) |
21.4 (70.5) |
23.2 (73.8) |
22.6 (72.7) |
17.4 (63.3) |
11.5 (52.7) |
4.5 (40.1) |
0.3 (32.5) |
11.3 (52.3) |
| المتوسط اليومي °س (°ف) | −3.7 (25.3) |
−3.4 (25.9) |
0.7 (33.3) |
7.0 (44.6) |
12.4 (54.3) |
15.7 (60.3) |
17.6 (63.7) |
16.9 (62.4) |
12.3 (54.1) |
7.4 (45.3) |
2.0 (35.6) |
−2.2 (28.0) |
6.9 (44.4) |
| متوسط الدنيا اليومية °س (°ف) | −6.4 (20.5) |
−6.6 (20.1) |
−3.5 (25.7) |
1.6 (34.9) |
6.4 (43.5) |
9.9 (49.8) |
11.9 (53.4) |
11.1 (52.0) |
7.1 (44.8) |
3.3 (37.9) |
−0.5 (31.1) |
−4.6 (23.7) |
2.5 (36.4) |
| الصغرى القياسية °س (°ف) | −34.6 (−30.3) |
−31.1 (−24.0) |
−23.6 (−10.5) |
−8.0 (17.6) |
−5.0 (23.0) |
−0.2 (31.6) |
−1.1 (30.0) |
0.1 (32.2) |
−5.1 (22.8) |
−11.1 (12.0) |
−19.3 (−2.7) |
−29.0 (−20.2) |
−34.6 (−30.3) |
| متوسط تساقط الأمطار mm (inches) | 22.0 (0.87) |
26.9 (1.06) |
29.8 (1.17) |
36.9 (1.45) |
60.3 (2.37) |
67.9 (2.67) |
80.3 (3.16) |
54.4 (2.14) |
59.1 (2.33) |
51.2 (2.02) |
44.1 (1.74) |
34.3 (1.35) |
567.2 (22.33) |
| Average precipitation days | 11.3 | 11.2 | 10.8 | 10.5 | 10.6 | 12.2 | 13.1 | 10.4 | 11.4 | 10.2 | 12.2 | 14.1 | 138 |
| Average rainy days | 7 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 7 | 8 | 8 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 9 | 6 | 93 |
| متوسط الرطوبة النسبية (%) | 90 | 90 | 80 | 70 | 70 | 75 | 75 | 75 | 85 | 85 | 90 | 95 | 82 |
| Mean monthly ساعات سطوع الشمس | 36.1 | 58.0 | 124.6 | 190.1 | 252.6 | 255.3 | 258.0 | 250.7 | 158.6 | 96.1 | 36.5 | 24.5 | 1٬741٫6 |
| Source: WeatherBase,[12] Climatebase.ru[13] and meteoblue.com[14] | |||||||||||||
| بيانات المناخ لـ Bialystok (Dojlidy), elevation: 148 m, 1961-1990 normals and extremes | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| الشهر | ينا | فب | مار | أبر | ماي | يون | يول | أغس | سبت | أكت | نوف | ديس | السنة |
| القصوى القياسية °س (°ف) | 10.9 (51.6) |
16.4 (61.5) |
21.8 (71.2) |
27.4 (81.3) |
30.1 (86.2) |
32.4 (90.3) |
34.8 (94.6) |
34.6 (94.3) |
29.8 (85.6) |
25.4 (77.7) |
16.8 (62.2) |
13.8 (56.8) |
34.8 (94.6) |
| متوسط القصوى اليومية °س (°ف) | −2.2 (28.0) |
−0.6 (30.9) |
4.4 (39.9) |
12.0 (53.6) |
18.4 (65.1) |
21.5 (70.7) |
22.6 (72.7) |
22.1 (71.8) |
17.4 (63.3) |
11.5 (52.7) |
4.6 (40.3) |
0.2 (32.4) |
11.0 (51.8) |
| المتوسط اليومي °س (°ف) | −4.8 (23.4) |
−3.8 (25.2) |
0.2 (32.4) |
6.7 (44.1) |
12.9 (55.2) |
16.1 (61.0) |
17.3 (63.1) |
16.3 (61.3) |
12.0 (53.6) |
7.2 (45.0) |
2.2 (36.0) |
−2.1 (28.2) |
6.7 (44.0) |
| متوسط الدنيا اليومية °س (°ف) | −7.7 (18.1) |
−6.8 (19.8) |
−3.4 (25.9) |
1.9 (35.4) |
7.0 (44.6) |
10.2 (50.4) |
11.7 (53.1) |
11.1 (52.0) |
7.6 (45.7) |
3.6 (38.5) |
−0.1 (31.8) |
−4.6 (23.7) |
2.5 (36.6) |
| الصغرى القياسية °س (°ف) | −35.4 (−31.7) |
−32.9 (−27.2) |
−24.0 (−11.2) |
−8.3 (17.1) |
−4.5 (23.9) |
0.7 (33.3) |
5.0 (41.0) |
0.2 (32.4) |
−5.1 (22.8) |
−9.9 (14.2) |
−20.7 (−5.3) |
−26.2 (−15.2) |
−35.4 (−31.7) |
| متوسط تساقط الأمطار mm (inches) | 35 (1.4) |
26 (1.0) |
31 (1.2) |
36 (1.4) |
56 (2.2) |
74 (2.9) |
80 (3.1) |
70 (2.8) |
52 (2.0) |
46 (1.8) |
46 (1.8) |
40 (1.6) |
592 (23.2) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 8.8 | 7.0 | 7.9 | 7.7 | 9.5 | 9.9 | 10.0 | 8.9 | 8.7 | 8.4 | 9.7 | 10.1 | 106.6 |
| Source: NOAA[15] | |||||||||||||
الثقافة والسياحة
الدين
Orthodox Church of the Holy Spirit
Eastern Orthodox Church of St. Nicholas in Lipowa Street
Transport
References
- ^ أ ب ت "Insygnia Białegostoku". Archived from the original on 2011-08-17. Retrieved 2011-08-01.
- ^ "Oficjalny portal miasta Białystok". bialystok.pl (in البولندية). Retrieved 23 December 2018.
- ^ "Local Data Bank". Statistics Poland. Retrieved 21 June 2020. Data for territorial unit 2061000.
- ^ قالب:Cite Oxford Dictionaries
- ^ "Białystok". The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language (5th ed.). HarperCollins. Retrieved 3 August 2019.
- ^ "Białystok". Collins English Dictionary. HarperCollins. Retrieved 3 August 2019.
- ^ قالب:Cite Merriam-Webster
- ^ "Miasta w Dokumencie Archiwalnym". Archived from the original on October 26, 2010. Retrieved 2011-04-05.
- ^ Nepokupnyj, A. P. (1970). Z movnoji spadščyny jatvjahiv. 5 (in الأوكرانية). Vol. 6. Movoznavstvo. pp. 18–25.
- ^ "Museums (Podlaskie Museum)". visitbialystok.com. Retrieved 2011-07-18.
- ^ أ ب "Białystok – Local history". Muzeum Historii Żydów Polskich. Archived from the original on 2011-10-07. Retrieved 2011-07-18.
- ^ "Weatherbase: Historical Weather for Białystok, Poland". Retrieved 2011-01-10.
- ^ "Climate Białystok – Poland". Retrieved 2011-01-31.
- ^ "Climate Białystok - Poland". Retrieved 2017-07-07.
- ^ "Bialystok (12295) - WMO Weather Station". NOAA. Retrieved December 27, 2018.
Further reading
- Łukasz Kaźmierczak, Trzy procent odmienności (Three percent of different) – article describing results of Polish census 2002 and minorities in Poland, citing census data (in پولندية)
- Janusz Żarnowski, "Społeczeństwo Drugiej Rzeczypospolitej 1918–1939", Warszawa 1973 (in پولندية)
- Eugeniusz Mironowicz, "Białoruś", Trio, Warszawa, 1999, ISBN 83-85660-82-8 (in پولندية)
- Yvette Walczak, "Let Her Go!", Naomi Roth Publishing, London, 2012, ISBN 978-0-9537585-2-4
وصلات خارجية
 بياويستوك travel guide from Wikivoyage
بياويستوك travel guide from Wikivoyage- Osiedla.Białystok.pl (in پولندية)
- VisitBiałystok.com (in پولندية, إنگليزية, and روسية)
- Białystok's official website at the Wayback Machine (archived فبراير 22, 2013) (in إنگليزية and پولندية)
- Official Site Białystok City Transport (in پولندية)
- Google Transit in Białystok
- قالب:JewishGen-LocalityPage
- Białystok at the B&F Compendium of Jewish Genealogy
- Pages using gadget WikiMiniAtlas
- CS1 البولندية-language sources (pl)
- CS1 الأوكرانية-language sources (uk)
- Short description is different from Wikidata
- Coordinates on Wikidata
- Articles containing بلاروسية-language text
- Pages with plain IPA
- Articles containing لتوانية-language text
- Pages using Lang-xx templates
- Articles containing يديشية-language text
- Articles containing روسية-language text
- Articles with hatnote templates targeting a nonexistent page
- Articles with پولندية-language sources (pl)
- Pages with empty portal template
- Articles with إنگليزية-language sources (en)
- Articles with روسية-language sources (ru)
- بياويستوك
- Cities and towns in Podlaskie Voivodeship
- المقاطعات المدن في پولندا
- Cities with powiat rights
- Podlachian Voivodeship
- Belostoksky Uyezd
- ڤويڤودية بياويستوك (1919–1939)
- Belastok Region
- Holocaust locations in Poland
![flag of the city [1]](/w/images/thumb/0/03/POL_Bia%C5%82ystok_flag.svg/100px-POL_Bia%C5%82ystok_flag.svg.png)
![seal of the city [1]](/w/images/thumb/1/1a/Bialystok_seal.png/100px-Bialystok_seal.png)
![shield of the city [1]](/w/images/thumb/1/19/POL_Bia%C5%82ystok_COA.svg/81px-POL_Bia%C5%82ystok_COA.svg.png)