جبل پيناتوبو
| جبل پيناتوبو Mount Pinatubo | |
|---|---|
 The eruption column of Mount Pinatubo on June 12, 1991, three days before the climactic eruption. | |
| أعلى نقطة | |
| الارتفاع | 1،486 m (4،875 ft)(current) 1,745 م (قبل ثوران 1991) |
| الإدراج | بركان نشط |
| التسمية | |
| لغة الاسم | Filipino |
| النطق | /ˌpiːnəˈtuːboʊ/ |
| الجغرافيا | |
| Location | لوزون |
| البلد | الفلپين |
| المنطقة | لوزون الوسطى |
| المقاطعات | |
| السلسلة الأم | جبال زامبالس |
| الجيولوجيا | |
| عمر الصخر | Between 635,000 ± 80,000 and 1.1 ± 0.09 million years[1] |
| نوع الجبل | بركان طبقي[2] |
| آخر ثوران | June 15, 1991[3] |
جزء من سلسلة عن |
|---|
| تاريخ الفلپين |
| خط زمني |
| الآثار |
جبل پيناتوبو (فيليپينو: Bundok Pinatubo/Bulkang Pinatubo؛ إنگليزية: Mount Pinatubo) هو بركان طبقي نشيط في جبال كابوسيلان في جزيرة لوزون، بالقرب من النقطة الثلاثية لـمقاطعات الفلپين زامبالس، تارلاك و پامپانگا.[4][5] تاريخ ثوراته لم يكن معروفاً للغالبية قبل الأنشطة البركانية في 1991. Pinatubo was heavily eroded, inconspicuous, and obscured from view. وكان مغطى بغابة كثيفة which supported a population of several thousand indigenous Aetas people.
The volcano's Plinian / Ultra-Plinian eruption on June 15, 1991 produced the second largest terrestrial eruption of the 20th century after the 1912 eruption of Novarupta in the Alaska Peninsula.[6] Complicating the eruption was the arrival of Typhoon Yunya (Diding), bringing a lethal mix of ash and rain to areas surrounding the volcano. Predictions at the onset of the climactic eruption led to the evacuation of tens of thousands of people from the surrounding areas, saving many lives. Surrounding areas were severely damaged by pyroclastic flows, ash deposits, and, subsequently, by the lahars caused by rainwaters re-mobilizing earlier volcanic deposits. This caused extensive destruction to infrastructure and changed river systems for years after the eruption.[6][7]
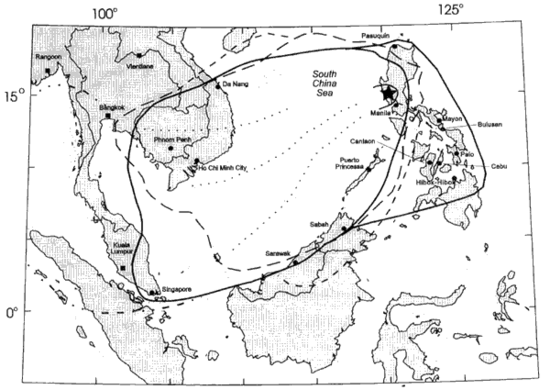
The effects of the eruption were felt worldwide. It ejected roughly 10،000،000،000 طن متري (1.1×1010 short ton) or 10 km3 (2.4 cu mi) of magma, and 20،000،000 طن متري (22،000،000 short ton) SO 2, bringing vast quantities of minerals and metals to the surface environment. It injected more particulate into the stratosphere than any eruption since Krakatoa in 1883. Over the following months, the aerosols formed a global layer of sulfuric acid haze. Global temperatures dropped by about 0.5 °C (0.9 °F) in the years 1991-93,[8] and ozone depletion temporarily increased substantially.[9]
استعراض المنطقة
البركان يقع على بعد 87 كم شمال غرب مانيلا، عاصمة الفلبين. Near Mount Pinatubo, the United States maintained two large military bases in the region. The U.S. Naval Base Subic Bay was 37 km (23 mi) south of Pinatubo, and the extent of Clark Air Base was just 14 km (8.7 mi) east of the volcano's summit.[10] The volcano's location on Luzon is in proximity to about 6 million people.[11]
التاريخ
ثوران 1991
| ثوران جبل بيناتوبو 1991 | |
|---|---|
 The eruption cloud shortly before the climactic eruption. | |
| التاريخ | June 15, 1991 |
| النوع | Ultra-Plinian |
| الموقع | منطقة لوزون الوسطى، لوزون، الفلپين |
| م.ت.ب | 6 |
| التأثير |
|
Vast quantities of minerals and metals were brought to the surface. Overall, introduced to the surface environment, was an estimated 800،000 t (880،000 short ton) of zinc, 600،000 t (660،000 short ton) of copper, 550،000 t (610،000 short ton) of chromium, 300،000 t (330،000 short ton) of nickel, and massive amounts of toxic heavy metals such as 100،000 t (110،000 short ton) of lead, 10،000 t (11،000 short ton) of arsenic, 1،000 t (1،100 short ton) of cadmium, and 800 t (880 short ton) of mercury.[14]
أعقاب ثوران 1991
انظر أيضاً
- List of active volcanoes in the Philippines
- List of inactive volcanoes in the Philippines
- List of volcanic eruptions by death toll
- List of potentially active volcanoes in the Philippines
- Timeline of volcanism on Earth
الهامش
- ^ "Pinatubo Volcano". The Philippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology (PHIVOLCS).
- ^ Pinatubo, Global Volcanism Program.
- ^ Mount Pinatubo Eruption - Mount Pinatubo
- ^ "Tarlac map". University of Texas in Austin Library. Retrieved 2011-08-02.
- ^ "Report of the Philippine Commission to the President, 1901 Vol. III", pg. 141. Government Printing Office, Washington, 1901.
- ^ أ ب "The Cataclysmic 1991 Eruption of Mount Pinatubo, Philippines". Retrieved 2007-04-09.
- ^ "Two Years of Lahars on the Western Flank of Mount Pinatubo: Initiation, Flow Processes, Deposits, and Attendant Geomorphic and Hydraulic Changes". USGS Publications. Retrieved 2012-03-07.
{{cite web}}: Cite uses deprecated parameter|authors=(help) - ^ Stephen Self; Jing-Xia Zhao; Rick E. Holasek; Ronnie C. Torres; Alan J. King (1999). "The Atmospheric Impact of the 1991 Mount Pinatubo Eruption". Retrieved July 25, 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|last-author-amp=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ "Mt. Pinatubo's cloud shades global climate". Science News. Retrieved 2010-03-07.
- ^ Tactical Pilotage Chart, Sheet K-11B, Defense Mapping Agency, Department of Defense, 1982.
- ^ Philippine Census
- ^ خطأ استشهاد: وسم
<ref>غير صحيح؛ لا نص تم توفيره للمراجع المسماةusgs - ^ Rosenberg, Matt. "Mount Pinatubo Eruption - The Volcanic Mount Pinatubo Eruption of 1991 that Cooled the Planet".
- ^ Garret, R.G. (November 2000). "Natural sources of metals in the environment". Human and Ecological Risk Assessment: an International Journal. 6 (6): 945–963. doi:10.1080/10807030091124383.
<ref> ذو الاسم "expoedu" المُعرّف في <references> غير مستخدم في النص السابق.مراجع
- Chakraborty P, et al. (2009). "Volcanic mesocyclones" (PDF). Nature. 458: 495–500. Bibcode:2009Natur.458..497C. doi:10.1038/nature07866.
- Decker, R. and Decker, B. (1997) Volcanoes, 3rd edition, WH Freeman, New York.
- McCormick, M. Patrick; et al. (1995). "Atmospheric effects of the Mt Pinatubo eruption". Nature. 373 (6513): 399–404. Bibcode:1995Natur.373..399M. doi:10.1038/373399a0.
- Rantucci, Giovanni (1994). Geological Disasters In The Philippines: The July 1990 Earthquake And The June 1991 Eruption of Mount Pinatubo. Description, effects and lessons learned. Philippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology (PHIVOLCS). ISBN 978-0-7881-2075-6. Retrieved 2009-08-15.
- Reilly, Benjamin (2009). Disaster and human history: case studies in nature, society and catastrophe. McFarland. ISBN 978-0-7864-3655-2.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Self S.; Zhao, Jing-Xia; Holasek, R.E.; Torres, R.C.; King, A.J. (1998). "Fire and Mud, Eruptions and Lahars of Mount Pinatubo, Philippines". Washington: Smithsonian Institution - Global Volcanism Program: 1126. Retrieved 2010-04-21.
The atmospheric impact of the 1991 Mount Pinatubo eruption
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help); Unknown parameter|editors=ignored (|editor=suggested) (help) - Scaillet, B. and Evans, B. W. (1999) The June 15, 1991 Eruption of Mount Pinatubo. I. Phase Equilibria and Pre-eruption P–T–fO2–fH2O Conditions of the Dacite Magma. Journal of Petrology, v. 40, 381–411.
- Stimac J.A., Goff F., Counce D., Larocque A.C.L., Hilton D.R. (2003), The crater lake and hydrothermal system of Mount Pinatubo, Philippines: evolution in the decade after eruption, Bulletin of Volcanology, v. 66, p. 149–167
- Wiesner, M.G., Wetzel, A. Catane, S.G., Listanco, E.L. and Mirabueno, H.T. (2004) Grain size, areal thickness distribution and controls on sedimentation of the 1991 Mount Pinatubo tephra layer in the South China Sea. Bulletin of Volcanology, v. 66, 226–242.
- Dhot, S. Mt Pinatubo Safety.
وصلات خارجية
- Mount Pinatubo Mount Pinatubo page
- Fire and Mud. Eruptions and Lahars of Mount Pinatubo, United States Geological Survey site
- Weather effects of the 1991 eruption EOS Volcanology.
- The Cataclysmic 1991 Eruption of Mount Pinatubo, Philippines. United States Geological Survey site
- Pinatubo, Philippines (volcanic images)
- CS1 errors: deprecated parameters
- CS1 errors: unsupported parameter
- Pages using infobox mountain with unknown parameters
- Pages using infobox mountain with language parameter
- Portal-inline template with redlinked portals
- Pages with empty portal template
- Articles containing فيليپينو-language text
- Pages using Lang-xx templates
- Articles containing إنگليزية-language text
- كوارث طبيعية في 1991
- 20th-century volcanic events
- براكين نشطة
- Active volcanoes of the Philippines
- 1991 disasters in the Philippines
- بحيرات فوهات براكين
- جبال الفلپين
- Natural disasters in the Philippines
- Stratovolcanoes of the Philippines
- Subduction volcanoes
- VEI-6 volcanoes
- Volcanic calderas of Southeast Asia
- Volcanic events
- براكين لوزون
- تضاريس پامپانگا
- تضاريس تارلاك
- تضاريس زامبالس