پپتيديز-4 ثنائي الپپتيديل
| عدِّل |
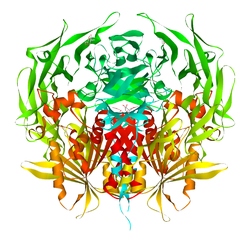
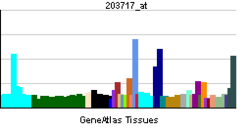
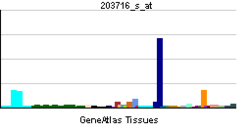
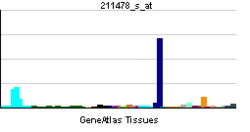
پپتيديز-4 ثنائي الپپتيديل Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP4)، ويعرف أيضاً باسم adenosine deaminase complexing protein 2 أو CD26 (تمايز عنقودي 26)، هو پروتين، يرمز إليه في البشر، بالجين DPP4.[1]
الوظيفة
يحمل هذا الپروتين رمز الجين DPP4 وهو إنزيم مستضدي يظهر على سطح معظم أنواع الخلايا وهو مرتبط بتنظيم المناعة، توصيل الإشارة والاستماتة الخلوية. وهو پروتين سكري غشائي داخلي وپپتيديز خارجي سريني cleaves cleaves X-proline dipeptides from the [[ترمينوس أميني|التريمونس الأميني في عديدات الپپتيد.
It is a rather indiscriminate enzyme for which a diverse range of substrates are known.[2] The substrates of CD26/DPPIV are proline(or alanine)-containing peptides and include growth factors, chemokines, neuropeptides, and vasoactive peptides.
DPP4 is related to attractin, FAP, DPP8 and DPP9.
DPP4 plays a major role in glucose metabolism. It is responsible for the degradation of incretins such as GLP-1.[3]
Furthermore, it appears to work as a suppressor in the development of cancer and tumours.[4][5][6]
CD26/DPPIV plays an important role in tumor biology, and is useful as a marker for various cancers, with its levels either on the cell surface or in the serum increased in some neoplasms and decreased in others.[7]
DPP-4 also binds the enzyme adenosine deaminase specifically and with high affinity. The significance of this interaction has yet to be established.
الدلالة السريرية
الفئة الجديدة من الأدوية الفموية الخافضة للسكر والمسماة مثبطات پپتيديز-4 ثنائي الپپتيديل تعمل على منع عمل هذا الانزيم، ويزيد العلاج من تأثير الإنسرتين في الجسم.[8]
الڤيروس المكلل الجديد المرتبط بسارس، قتل ثمانية من 14 شخص أصيبوا بالعدوى. وُجد هذا الڤيروس معلق بپپتيديز-4 ثنائي الپپتيديل. وُجد پپتيديز-4 ثنائي الپپتيديل على سطح خلايا الممرات الهوائية (مثل الرئة) والكلى. قد يتمكن العلماء من استخدام هذه الميزة لمنع الڤيروس من دخول الخلية.[9]
انظر أيضاً
المصادر
- ^ Kameoka J, Tanaka T, Nojima Y, Schlossman SF, Morimoto C (1993). "Direct association of adenosine deaminase with a T cell activation antigen, CD26". Science. 261 (5120): 466–9. doi:10.1126/science.8101391. PMID 8101391.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Chen X (2006). "Biochemical properties of recombinant prolyl dipeptidases DPP-IV and DPP8". Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. 575: 27–32. doi:10.1007/0-387-32824-6_3. ISBN 978-0-387-29058-4. PMID 16700505.
- ^ Barnett A (2006). "DPP-4 inhibitors and their potential role in the management of type 2 diabetes". Int. J. Clin. Pract. 60 (11): 1454–70. doi:10.1111/j.1742-1241.2006.01178.x. PMID 17073841.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Pro B, Dang N (2004). "CD26/dipeptidyl peptidase IV and its role in cancer". Histol Histopathol. 19 (4): 1345–51. PMID 15375776.
- ^ Masur K; et al. (2006). "DPPIV inhibitors extend GLP-2 mediated tumour promoting effects on intestinal cancer cells". Regul Pept. 137 (3): 147–55. doi:10.1016/j.regpep.2006.07.003. PMID 16908079.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help) - ^ Wesley UV; et al. (2005). "Dipeptidyl peptidase inhibits malignant phenotype of prostate cancer cells by blocking basic fibroblast growth factor signaling pathway". Cancer Res. 65 (4): 1325–34. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-1852. PMID 15735018.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help) - ^ Havre PA, Abe M, Urasaki Y, Ohnuma K, Morimoto C, Dang NH (2008). "The role of CD26/dipeptidyl peptidase IV in cancer". Front. Biosci. 13 (13): 1634–45. doi:10.2741/2787. PMID 17981655.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Rosenstock J, Zinman B (2007). "Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors and the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus". Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 14 (2): 98–107. doi:10.1097/MED.0b013e3280a02f65. PMID 17940427.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Raj VS, Mou H, Smits SL, Dekkers DH, Müller MA, Dijkman R, Muth D, Demmers JA, Zaki A, Fouchier RA, Thiel V, Drosten C, Rottier PJ, Osterhaus AD, Bosch BJ, Haagmans BL (2013). "Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 is a functional receptor for the emerging human coronavirus-EMC". Nature. ScienceNews. 495 (7440): 251–4. doi:10.1038/nature12005. PMID 23486063.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|laysource=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|laysummary=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
وصلات خارجية
- The MEROPS online database for peptidases and their inhibitors: S09.003
- MeSH Dipeptidyl-Peptidase+IV
- قالب:UTGlucagon
قراءات إضافية
- Ansorge S, Bühling F, Kähne T; et al. (1997). "CD26/dipeptidyl peptidase IV in lymphocyte growth regulation". Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 421: 127–40. PMID 9330689.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Reinhold D, Kähne T, Steinbrecher A; et al. (2003). "The role of dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DP IV) enzymatic activity in T cell activation and autoimmunity". Biol. Chem. 383 (7–8): 1133–8. doi:10.1515/BC.2002.123. PMID 12437097.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Sato K, Dang NH (2003). "CD26: a novel treatment target for T-cell lymphoid malignancies? (Review)". Int. J. Oncol. 22 (3): 481–97. PMID 12579300.
- de Meester I, Lambeir AM, Proost P, Scharpé S (2003). "Dipeptidyl peptidase IV substrates. An update on in vitro peptide hydrolysis by human DPPIV". Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. 524: 3–17. doi:10.1007/0-306-47920-6_1. ISBN 0-306-47717-3. PMID 12675218.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Koch S, Anthonsen D, Skovbjerg H, Sjöström H (2003). "On the role of dipeptidyl peptidase IV in the digestion of an immunodominant epitope in celiac disease". Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. 524: 181–7. doi:10.1007/0-306-47920-6_22. ISBN 0-306-47717-3. PMID 12675238.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Pro B, Dang NH (2005). "CD26/dipeptidyl peptidase IV and its role in cancer". Histol. Histopathol. 19 (4): 1345–51. PMID 15375776.