الصفحة قالب:Infobox probability distribution/styles.css ليس بها محتوى.
Binomial distribution
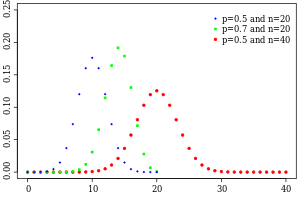
Probability mass function
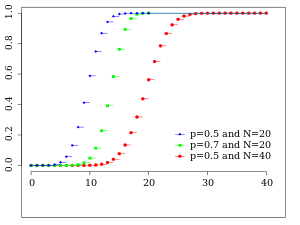
Cumulative distribution function
الترميز
B
(
n
,
p
)
{\displaystyle B(n,p)}
الوسائط
n
∈
{
0
,
1
,
2
,
…
}
{\displaystyle n\in \{0,1,2,\ldots \}}
p
∈
[
0
,
1
]
{\displaystyle p\in [0,1]}
الحامل
k
∈
{
0
,
1
,
…
,
n
}
{\displaystyle k\in \{0,1,\ldots ,n\}}
PMF
(
n
k
)
p
k
(
1
−
p
)
n
−
k
{\displaystyle {\binom {n}{k}}p^{k}(1-p)^{n-k}}
CDF
I
1
−
p
(
n
−
k
,
1
+
k
)
{\displaystyle I_{1-p}(n-k,1+k)}
المتوسط
n
p
{\displaystyle np}
أوسط
⌊
n
p
⌋
{\displaystyle \lfloor np\rfloor }
⌈
n
p
⌉
{\displaystyle \lceil np\rceil }
منوال
⌊
(
n
+
1
)
p
⌋
{\displaystyle \lfloor (n+1)p\rfloor }
⌈
(
n
+
1
)
p
⌉
−
1
{\displaystyle \lceil (n+1)p\rceil -1}
تباين
n
p
(
1
−
p
)
{\displaystyle np(1-p)}
تخالف
1
−
2
p
n
p
(
1
−
p
)
{\displaystyle {\frac {1-2p}{\sqrt {np(1-p)}}}}
تدبب زائد
1
−
6
p
(
1
−
p
)
n
p
(
1
−
p
)
{\displaystyle {\frac {1-6p(1-p)}{np(1-p)}}}
الاعتلاج
1
2
log
2
(
2
π
e
n
p
(
1
−
p
)
)
+
O
(
1
n
)
{\displaystyle {\frac {1}{2}}\log _{2}\left(2\pi enp(1-p)\right)+O\left({\frac {1}{n}}\right)}
shannons . For nats , use the natural log in the log. MGF
(
1
−
p
+
p
e
t
)
n
{\displaystyle (1-p+pe^{t})^{n}}
CF
(
1
−
p
+
p
e
i
t
)
n
{\displaystyle (1-p+pe^{it})^{n}}
PGF
G
(
z
)
=
[
(
1
−
p
)
+
p
z
]
n
{\displaystyle G(z)=[(1-p)+pz]^{n}}
معلومات فيشر
g
n
(
p
)
=
n
p
(
1
−
p
)
{\displaystyle g_{n}(p)={\frac {n}{p(1-p)}}}
n
{\displaystyle n}
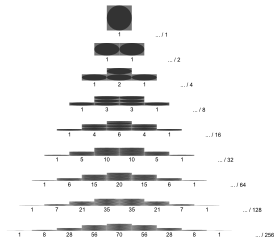
Binomial distribution for
p
=
0.5
{\displaystyle p=0.5}
with
n and
k as in
Pascal's triangle The probability that a ball in a
Galton box with 8 layers (
n = 8) ends up in the central bin (
k = 4) is
70
/
256
{\displaystyle 70/256}
.
توزيع احتمالي ثنائي هو توزيع لتجربة عشوائية لها ناتجان فقط أحدهما نجاح التجربة والآخر فشلها ويكون الشرط الأساسي أن احتمال النجاح لا يتأثر بتكرار التجربة ، أمثلة : رمي قطعة نقود ، الإحصاءات أو الأسئلة التي تعتمد الإجابة لا أو نعم.
بتعبير آخر التوزيع الاحتمالي ثنائي الحد هو تكرار لتجربة برنولي (انظر توزيع برنولي ).
خصائص التوزيع الثنائي يتميز التوزيع الثنائى بعدة خصائص هي:
تتكون التجربة من أكثر من محاولة. إذا تكونت التجربة من محاولة واحدة ،فإننا في تجربة توزيع برنولي
استقلال المحاولات عن بعضها البعض أي ثبات احتمال النجاح p ومن ثم احتمال الفشل q.
هذه المحاولات جميعا متماثلة ومستقلة.
احتمال النجاح ثابت في كل محاولة. قالب:بعض التوزيعات الاحتمالية الشائعة بمتغير واحد
F
(
k
;
n
,
p
)
=
Pr
(
X
≤
k
)
=
I
1
−
p
(
n
−
k
,
k
+
1
)
=
(
n
−
k
)
(
n
k
)
∫
0
1
−
p
t
n
−
k
−
1
(
1
−
t
)
k
d
t
.
{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}F(k;n,p)&=\Pr(X\leq k)\\&=I_{1-p}(n-k,k+1)\\&=(n-k){n \choose k}\int _{0}^{1-p}t^{n-k-1}(1-t)^{k}\,dt.\end{aligned}}}
Some closed-form bounds for the cumulative distribution function are given below .
Example Suppose a biased coin comes up heads with probability 0.3 when tossed. What is the probability of achieving 0, 1,..., 6 heads after six tosses?
Pr
(
0
heads
)
=
f
(
0
)
=
Pr
(
X
=
0
)
=
(
6
0
)
0.3
0
(
1
−
0.3
)
6
−
0
=
0.117649
{\displaystyle \Pr(0{\text{ heads}})=f(0)=\Pr(X=0)={6 \choose 0}0.3^{0}(1-0.3)^{6-0}=0.117649}
Pr
(
1
heads
)
=
f
(
1
)
=
Pr
(
X
=
1
)
=
(
6
1
)
0.3
1
(
1
−
0.3
)
6
−
1
=
0.302526
{\displaystyle \Pr(1{\text{ heads}})=f(1)=\Pr(X=1)={6 \choose 1}0.3^{1}(1-0.3)^{6-1}=0.302526}
Pr
(
2
heads
)
=
f
(
2
)
=
Pr
(
X
=
2
)
=
(
6
2
)
0.3
2
(
1
−
0.3
)
6
−
2
=
0.324135
{\displaystyle \Pr(2{\text{ heads}})=f(2)=\Pr(X=2)={6 \choose 2}0.3^{2}(1-0.3)^{6-2}=0.324135}
Pr
(
3
heads
)
=
f
(
3
)
=
Pr
(
X
=
3
)
=
(
6
3
)
0.3
3
(
1
−
0.3
)
6
−
3
=
0.18522
{\displaystyle \Pr(3{\text{ heads}})=f(3)=\Pr(X=3)={6 \choose 3}0.3^{3}(1-0.3)^{6-3}=0.18522}
Pr
(
4
heads
)
=
f
(
4
)
=
Pr
(
X
=
4
)
=
(
6
4
)
0.3
4
(
1
−
0.3
)
6
−
4
=
0.059535
{\displaystyle \Pr(4{\text{ heads}})=f(4)=\Pr(X=4)={6 \choose 4}0.3^{4}(1-0.3)^{6-4}=0.059535}
Pr
(
5
heads
)
=
f
(
5
)
=
Pr
(
X
=
5
)
=
(
6
5
)
0.3
5
(
1
−
0.3
)
6
−
5
=
0.010206
{\displaystyle \Pr(5{\text{ heads}})=f(5)=\Pr(X=5)={6 \choose 5}0.3^{5}(1-0.3)^{6-5}=0.010206}
Pr
(
6
heads
)
=
f
(
6
)
=
Pr
(
X
=
6
)
=
(
6
6
)
0.3
6
(
1
−
0.3
)
6
−
6
=
0.000729
{\displaystyle \Pr(6{\text{ heads}})=f(6)=\Pr(X=6)={6 \choose 6}0.3^{6}(1-0.3)^{6-6}=0.000729}
[1] Mean If X ~ B (n , p ), that is, X is a binomially distributed random variable, n being the total number of experiments and p the probability of each experiment yielding a successful result, then the expected value of X is:[2]
E
[
X
]
=
n
p
.
{\displaystyle \operatorname {E} [X]=np.}
For example, if n = 100, and p = 1/4, then the average number of successful results will be 25.
Proof: We calculate the mean, μ , directly calculated from its definition
μ
=
∑
i
=
0
n
x
i
p
i
,
{\displaystyle \mu =\sum _{i=0}^{n}x_{i}p_{i},}
and the binomial theorem :
μ
=
∑
k
=
0
n
k
(
n
k
)
p
k
(
1
−
p
)
n
−
k
=
n
p
∑
k
=
0
n
k
(
n
−
1
)
!
(
n
−
k
)
!
k
!
p
k
−
1
(
1
−
p
)
(
n
−
1
)
−
(
k
−
1
)
=
n
p
∑
k
=
1
n
(
n
−
1
)
!
(
(
n
−
1
)
−
(
k
−
1
)
)
!
(
k
−
1
)
!
p
k
−
1
(
1
−
p
)
(
n
−
1
)
−
(
k
−
1
)
=
n
p
∑
k
=
1
n
(
n
−
1
k
−
1
)
p
k
−
1
(
1
−
p
)
(
n
−
1
)
−
(
k
−
1
)
=
n
p
∑
ℓ
=
0
n
−
1
(
n
−
1
ℓ
)
p
ℓ
(
1
−
p
)
(
n
−
1
)
−
ℓ
with
ℓ
:=
k
−
1
=
n
p
∑
ℓ
=
0
m
(
m
ℓ
)
p
ℓ
(
1
−
p
)
m
−
ℓ
with
m
:=
n
−
1
=
n
p
(
p
+
(
1
−
p
)
)
m
=
n
p
{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\mu &=\sum _{k=0}^{n}k{\binom {n}{k}}p^{k}(1-p)^{n-k}\\&=np\sum _{k=0}^{n}k{\frac {(n-1)!}{(n-k)!k!}}p^{k-1}(1-p)^{(n-1)-(k-1)}\\&=np\sum _{k=1}^{n}{\frac {(n-1)!}{((n-1)-(k-1))!(k-1)!}}p^{k-1}(1-p)^{(n-1)-(k-1)}\\&=np\sum _{k=1}^{n}{\binom {n-1}{k-1}}p^{k-1}(1-p)^{(n-1)-(k-1)}\\&=np\sum _{\ell =0}^{n-1}{\binom {n-1}{\ell }}p^{\ell }(1-p)^{(n-1)-\ell }&&{\text{with }}\ell :=k-1\\&=np\sum _{\ell =0}^{m}{\binom {m}{\ell }}p^{\ell }(1-p)^{m-\ell }&&{\text{with }}m:=n-1\\&=np(p+(1-p))^{m}\\&=np\end{aligned}}}
التاريخ This distribution was derived by James Bernoulli . He considered the case where p = r /(r + s ) where p is the probability of success and r and s are positive integers. Blaise Pascal had earlier considered the case where p = 1/2.
See also الهامش
^ Hamilton Institute. "The Binomial Distribution" October 20, 2010.
^ See Proof Wiki
^ Mandelbrot, B. B., Fisher, A. J., & Calvet, L. E. (1997). A multifractal model of asset returns. 3.2 The Binomial Measure is the Simplest Example of a Multifractal
مراجع
Discrete
with finite with infinite
Continuous
supported on a supported on a supported with support
Mixed
Multivariate Directional Degenerate singular العائلات


![{\displaystyle p\in [0,1]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/33c3a52aa7b2d00227e85c641cca67e85583c43c)














![{\displaystyle G(z)=[(1-p)+pz]^{n}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/ad93fbb1208a6637ccd78540a9ddfc2e65a91ee2)












![{\displaystyle \operatorname {E} [X]=np.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/3f16b365410a1b23b5592c53d3ae6354f1a79aff)

