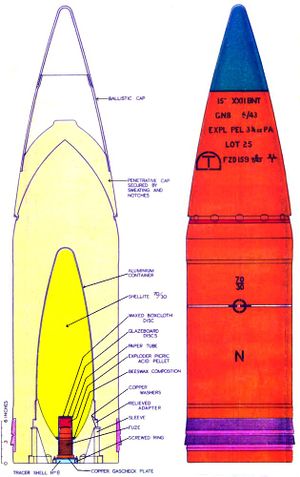
قذيفة خارقة للدروع
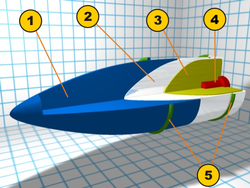
1 Light weight ballistic cap
2 Steel alloy piercing shell
3 Desensitized bursting charge (TNT, حمض الپيكريك وتراينيتروفنول Picric acid & Trinitrophenol, RDX...)
4 Fuse (معدة بتأخير لتنفجر داخل الهدف)
5 Bourrelet (front) and driving band (rear)
القذيفة الخارقة للدروع armor-piercing shell هي نوع من الذخيرة مصممة لاختراق درع. ومنذ عقد 1860 إلى عقد 1950، كان الاستخدام الرئيسي للمقذوفات الخارقة للدروع هو هزيمة الدرع السميك الذي يحمله العديد من السفن البحرية. ومنذ عقد 1920 فصاعداً، أصبحت الأسلحة الخارقة للدروع أساسية للمهام المضادة للدبابات.
An armor-piercing shell must withstand the shock of punching through armor plating. Shells designed for this purpose have a greatly strengthened case with a specially hardened and shaped nose, and a much smaller bursting charge. Some smaller-caliber AP shells have an inert filling, or incendiary charge in place of the HE bursting charge. The AP shell is now little used in naval warfare, as modern warships have little or no armor protection[بحاجة لمصدر], but it remains the preferred round in tank warfare, as it has a greater "first-hit kill" probability than a high explosive anti-tank (HEAT) round, especially against a target with composite armor, and because of higher muzzle velocity, is also more accurate than a HEAT round.
Armor-piercing cartridges are also available as small arms ammunition, primarily for use as an anti-matériel round.
الحرب العالمية الثانية
أمثلة لقذائف خارقة للدروع
| Round | المقذوف | الوزن |
|---|---|---|
| M2 | .30-06 Springfield | 163 grain |
| M61 | 7.62x51mm NATO | 150.5 grain[1] |
| FN P80 | 7.62x51mm NATO | 150 grain |
| AP485 | .338 Lapua Magnum | 248 grain[2] |
| M995 | 5.56x45mm NATO | 52 grain[1] |
| S.m.K. | 7.92x57 mm Mauser | 178.25 grain |
طالع أيضاً
المصادر
- ^ أ ب "Ballistics Chart for Military Ammunition". Gun Shots. Retrieved 2008-12-04.
- ^ "The original .338 Lapua Magnum" (PDF). Lapua. Retrieved 2008-12-04.