سرطان القولون والمستقيم
| سرطان القولون والمستقيم | |
|---|---|
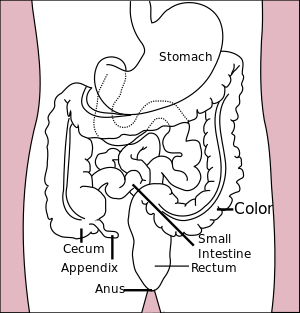 | |
| رسم توضيحي للمعدة والقولون والمستقيم | |
| التبويب والمصادر الخارجية | |
| ICD-10 | C18.-C20. |
| ICD-9-CM | 153.0-154.1 |
| ICD-O | M8140/3 (95% of cases) |
| OMIM | 114500 |
| DiseasesDB | 2975 |
| MedlinePlus | 000262 |
| eMedicine | med/413 med/1994 ped/3037 |
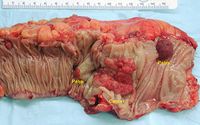
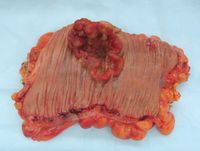
سرطان القولون والمستقيم Colorectal cancer، ويسمى أيضاً سرطان القولون أو سرطان الأمعاء الغليظةlarge bowel cancer، بما فيها مختلف أنواع النمو السرطاني في القولون, المستقيم والزائدة. ويتسبب في نحو 655,000 وفاة في العالم كل سنة، وهو ثالث أمراض السرطان شيوعاً وثاني أكبر متسبب في وفاة متعلقة بالسرطان في العالم الغربي.[1] ويـُعتـَقـَد أن العديد من سرطانات القولون والمستقيم ينشأوا من سلائل Polyps ذات ورم غدي Adenoma في القولون. هذه الأشكال من النمو الشبيه بالفطر عادة ما يكونوا حميدين، ولكن بعضهم قد يتطور إلى سرطان مع مرور الوقت. في معظم الأوقات، تشخيص سرطان قولون متموضع يكون من خلال تنظير القولون. ويكون العلاج عادة جراحي ، ويتبعه في الكثير من الحالات علاج كيماوي.
بالتشخيص المبكر ممكن شفاء أكثر من 90% من المصابين. على عكس المراحل المتأخرة التى لا تصل فيها نسبة الشفاء الى 37%. أكبر مشكلة أن الأعراض شائعة جدا ويتم إعتبارها بسهولة أعراض بواسير او قولون عصبى او عسر هضم مما يؤدى إلى تفاقم المشكلة وتضيع فرصة التشخيص المبكر والشفاء. بل أن 90% من مرضى سرطان المستقيم يعانون فعلا من وجود بواسير شرجية مع السرطان.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
الأعراض
الأعراض الموضعية
البواسير – نزيف بسيط- هرش- الم خفيف داخلى · كثرة الغازات
· تغير في الطبيعة (إمساك حديث مستمر)
· دم في البراز
· آلام مستمرة في البطن
· تغير في شكل البراز
· الإحساس بعدم التفريغ غير الكامل للفضلات
· نقص الوزن
· الإجهاد السريع
الأعراض البنيوية (المجموعية Systemic)
الأعراض النقيلية Metastatic
عوامل الخطر
الكحول
تقرير مؤتمرWCRF المسمى الغذاء والتغذية والنشاط الرياضي وتجنب السرطان: منظور عالمي يجد أن الأدلة "مقنعة" أن المشروبات الكحولية تزيد من خطر سرطان القولون والمستقيم في الرجال.[2]
التشخيص، التنظير الشعاعي والمراقبة
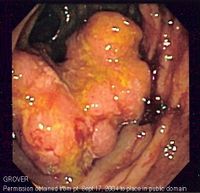
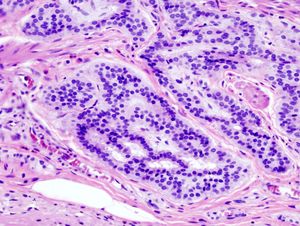
پاثولوجيا
المراحل
نظام ديوكس Dukes
Dukes classification, first proposed by Dr Cuthbert E. Dukes in 1932, identifies the stages as:[3]
- A - Tumour confined to the intestinal wall
- B - Tumour invading through the intestinal wall
- C - With lymph node(s) involvement (this is further subdivided into C1 lymph node involvement where the apical node is not involved and C2 where the apical lymph node is involved)
- D - With distant metastasis
نظام TNM
The most common current staging system is the TNM (for tumors/nodes/metastases) system, though many doctors still use the older Dukes system. The TNM system assigns a number[4]:
- T - The degree of invasion of the intestinal wall
- T0 - no evidence of tumor
- Tis- cancer in situ (tumor present, but no invasion)
- T1 - invasion through muscularis mucosa into submucosa
- T2 - invasion through submucosa into the muscularis propria (i.e. proper muscle of the bowel wall)
- T3 - invasion through the muscularis propria into subserosa but not to any neighbouring organs or tissues
- T4 - invasion of surrounding structures (e.g. bladder) or with tumour cells on the free external surface of the bowel
- N - the degree of lymphatic node involvement
- N0 - no lymph nodes involved
- N1 - one to three nodes involved
- N2 - four or more nodes involved
- M - the degree of metastasis
- M0 - no metastasis
- M1 - metastasis present
تجميعات مراحل AJCC
The stage of a cancer is usually quoted as a number I, II, III, IV derived from the TNM value grouped by prognosis; a higher number indicates a more advanced cancer and likely a worse outcome.
- Stage 0
- Tis, N0, M0
- Stage I
- T1, N0, M0
- T2, N0, M0
- Stage IIA
- T3, N0, M0
- Stage IIB
- T4, N0, M0
- Stage IIIA
- T1, N1, M0
- T2, N1, M0
- Stage IIIB
- T3, N1, M0
- T4, N1, M0
- Stage IIIC
- Any T, N2, M0
- Stage IV
- Any T, Any N, M1
نشأة المرض
المعالجة
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
الجراحة
العلاج الكيماوي
العلاج بالإشعاع
العلاج المناعي
اللقاح
المآل
المتابعة
الوقاية
المسح الصحي
نمط الحياة والتغذية
الوقاية الكيميائية
انظر أيضاً
المصادر
- ^ "Cancer". World Health Organization. 2006. Retrieved 2007-05-24.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ WCRF Food, Nutrition, Physical Activity and the Prevention of Cancer: a Global Perspective
- ^ Dukes CE. The classification of cancer of the rectum. Journal of Pathological Bacteriology 1932;35:323.
- ^
Wittekind, Ch; Sobin, L. H. (2002). TNM classification of malignant tumours. New York: Wiley-Liss. ISBN 0-471-22288-7.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
وصلات خارجية