يهودا
Coordinates: 31°41′56″N 35°18′23″E / 31.69889°N 35.30639°E
يهودا ( /dʒuːˈdiː.ə/؛[1] from بالعبرية: יהודה، الفصحى Yəhuda, Tiberian Yəhûḏāh, باليونانية: Ἰουδαία, قالب:Grc-tr؛ لاتينية: Iūdaea, العربية: يهودا، Yahudia؛ إنگليزية: Judea أو Judæa) هي the ancient biblical, Roman, and modern name of the mountainous southern part of Palestine. The name originates from the Hebrew, Canaanite and later neo-Babylonian and Persian name "Yehudah" or "Yehud" for the biblical Israelite tribe of Judah (Yehudah) and associated Kingdom of Judah, which the 1906 Jewish Encyclopedia dates from 934 until 586 BCE.[2] The name of the region continued to be incorporated through the Babylonian conquest, Persian, Hellenistic, and Roman periods as Yehud, Yehud Medinata, Hasmonean Judea, and consequently Herodian Judea and Roman Judea, respectively.
As a consequence of the Bar Kokhba revolt, in 135 CE the region was renamed and merged with Roman Syria to form Syria Palaestina by the victorious Roman Emperor Hadrian. A large part of Judea was included in Jordanian West Bank between 1948 and 1967 (i.e., the "West Bank" of the Kingdom of Jordan).[3][4] The term Judea as a geographical term was revived by the Israeli government in the 20th century as part of the Israeli administrative district name Judea and Samaria Area for the territory generally referred to as the West Bank.[5]
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Etymology
The name Judea is a Greek and Roman adaptation of the name "Judah", which originally encompassed the territory of the Israelite tribe of that name and later of the ancient Kingdom of Judah. Nimrud Tablet K.3751, dated c.733 BCE, is the earliest known record of the name Judah (written in Assyrian cuneiform as Yaudaya or KUR.ia-ú-da-a-a).
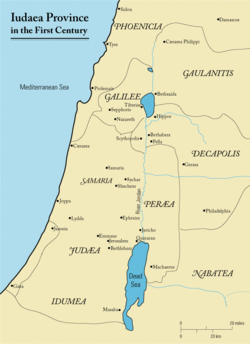
الحدود التاريخية
الجغرافيا
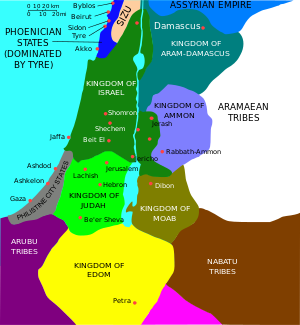
التاريخ
العصر الحديدي المبكر
الفترتان الفارسية والهلينية
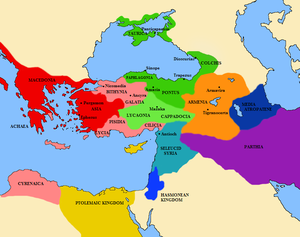
The Babylonian Empire fell to the conquests of Cyrus the Great in 539 BCE.[6]
الفتح الروماني
ثورة بار كوخبا
Again 70 years later, the Jewish population revolted under the leadership of Simon bar Kokhba and established the last Kingdom of Israel, which lasted three years, before the Romans managed to conquer the province for good, at a high cost in terms of manpower and expense.
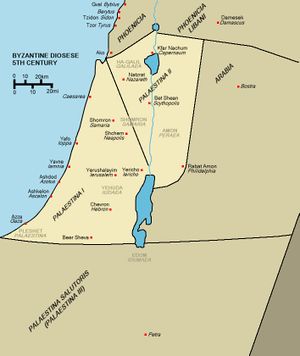
الفترة البيزنطية
Timeline
- 11th century BCE–930 BCE — part of the Kingdom of Israel
- 930 BCE–586 BCE — Kingdom of Judah
- 586 BCE–539 BCE — Babylonian Empire
- 539 BCE–332 BCE — Persian Empire
- 332 BCE–305 BCE — Macedonian Empire of Alexander the Great
- 305 BCE–198 BCE — Ptolemaics
- 198 BCE–141 BCE — Seleucids
- 141 BCE–37 BCE — The Hasmonean state in Israel established by the Maccabees, after 63 BCE under Roman supremacy
- 63 BCE — Pompey's conquest of Jerusalem
- 37 BCE–132 CE — Herodian Dynasty ruling Judea as vassal kings under Roman supremacy (37 BCE–4 BCE Herod the Great, 4 BCE–6 CE Herod Archelaus, 41–44 CE Agrippa I), interchanging with direct Roman rule (6–41, 44–132)
- c. 25 BCE — Caesarea Maritima is built by Herod the Great
- 6 CE — Census of Quirinius, too late to correspond to census related to Jesus' birth
- 26–36 — Pontius Pilate prefect of Roman Judea during the Crucifixion of Jesus
- 66–73 — First Jewish–Roman War, includes Destruction of the Second Temple in 70
- 115–117 — Kitos War
- 132–135 — Bar Kokhba's revolt
- 135 — Emperor Hadrian reverts to the name Syria Palaestina first used by Herodotus
انظر أيضاً
الهامش
- ^ "Book of Mormon Pronunciation Guide". LDS.org. Retrieved 2012-02-25.
- ^ "Judah, Kingdom of". Jewish Encyclopedia. Retrieved 2014-04-10.
- ^ A History of the Israeli-Palestinian Conflict – Mark A. Tessler – Google Books. Books.google.com. Retrieved 2012-12-31.
- ^ http://www.nytimes.com/2008/12/05/world/middleeast/05mideast.html?_r=0
- ^ Neil Caplan (19 September 2011). The Israel-Palestine Conflict: Contested Histories. John Wiley & Sons. p. 8. ISBN 978-1405175395.
- ^ "The Persians". Jewish Virtual Library. Retrieved 2009-06-09.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
وصلات خارجية
- Judea and civil war
- The subjugation of Judea
- Judaea 6–66 CE
- Judea photos
- The Jewish History Resource Center Project of the Dinur Center for Research in Jewish History, Hebrew University of Jerusalem
- Articles with hatnote templates targeting a nonexistent page
- صفحات بالمعرفة فيها قوالب حماية خاطئة
- Semi-protected
- صفحات بالمعرفة فيها قوالب حماية خطأ
- Coordinates on Wikidata
- Articles containing عبرية-language text
- Articles containing Greek-language text
- Articles containing لاتينية-language text
- Articles containing explicitly cited عربية-language text
- Articles containing إنگليزية-language text
- منطقة يهودا والسامرا
- Judea
- Ancient Jewish Greek history
- Ancient Jewish history of Roman Republic and Roman Empire eras
- Ancient Jewish Persian history
- Geography of Israel
- Biblical places
- Geography of the Palestinian territories
- أماكن مذكورة في التوراة
- مناطق تاريخية
- Judea and Samaria Area
- أماكن مذكورة في الإنجيل
- مناطق إسرائيل